I just find this incredible!
Firstly, I am simply going to post three YouTube videos of this amazing feat by NASA.
The first by Associated Press at less than two minutes:
And the next two from NASA with the second at just over an hour long:
and the third at over three hours long:
Then I am going to republish, hopefully with permission, an article from Nature that further explains what has just happened:
ooOOoo
Special delivery! Biggest-ever haul of asteroid dust and rock returns to Earth
Samples collected by NASA’s OSIRIS-REx mission excite scientists with their potential to reveal secrets of the Solar System.
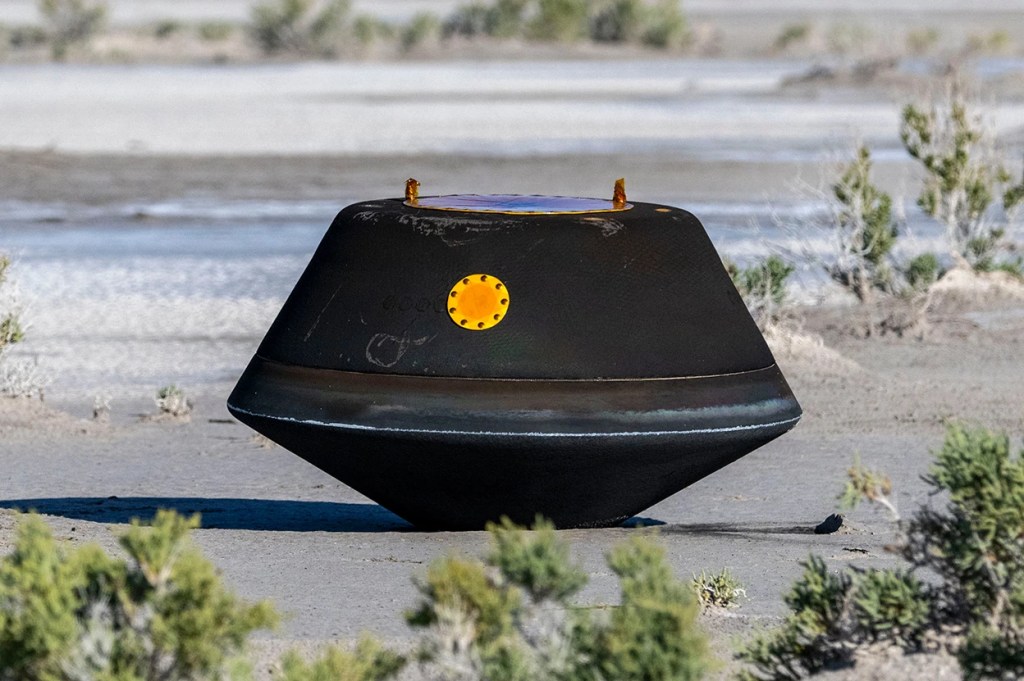
The OSIRIS-REx sample capsule, which contains pieces of the asteroid Bennu, landed safely in the Utah desert on 24 September. Credit: Keegan Barber/NASA via Getty
Dugway Proving Ground, Utah
A saucer-shaped capsule parachuted down gently in the Utah desert today, after a years-long journey through space. Its cargo is a precious collection of rocks and dust from the asteroid Bennu — the first time NASA has ever brought pieces of this type of celestial object back to Earth.
Over the coming days, NASA will fly the bits of Bennu to the Johnson Space Center in Houston, Texas. There, curators will carefully disassemble the container and begin analysing the chemistry and mineralogy of the pristine samples — which might hold clues to the origins of the Solar System.
“I feel like a kid on Christmas Eve who is just too excited to go to sleep,” says Michelle Thompson, a planetary scientist at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, and a member of the ‘quick look’ team who will have the first chance to study the rocks.
Space hoover
The material comes from the US$1.2-billion OSIRIS-REx (Origins, Spectral Interpretation, Resource Identification, Security-Regolith Explorer) mission, which launched in 2016 and arrived at Bennu in 2018. It spent nearly two years studying the dark-coloured, diamond-shaped asteroid before extending its robotic arm to the rocky surface, blasting it with a puff of gas and collecting the dust and rocks it kicked up. That ‘fist bump’ hoovered up so much material that pieces of rock got jammed in the collection mechanism, allowing some of the smaller pebbles to escape. Watching some of those samples get away was “heart breaking”, says Dante Lauretta, a planetary scientist at the University of Arizona in Tucson who was the first principal investigator of the OSIRIS-REx mission.
Still, the spacecraft managed to collect around 250 grams of rocks and dirt — a large cupful — including several chunks that are at least one centimetre long. It is by far the largest amount of material ever brought back from an asteroid. The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) had previously collected less than one milligram from the asteroid Itokawa in 2005, and 5.4 grams from the asteroid Ryugu in 2019.
Bringing planetary samples back to Earth allows researchers to use cutting-edge laboratory techniques to study what the rocks are made of. The NASA curation team planned to put the Bennu samples into an atmosphere of pure nitrogen soon after the capsule touched down, to reduce the potential for contamination. That will enable scientists to study the asteroid’s geology and chemistry, preserved all the way back to the formation of the Solar System, more than 4.5 billion years ago. The pristine material hasn’t been altered by passing through Earth’s atmosphere, as happens with meteorites. “The thing that will really be different about this sample is we’ll have that chain of custody of keeping it protected from Earth’s atmosphere,” says Nicole Lunning, the mission’s lead sample curator at the Johnson Space Center.
Precious cargo
Bennu is a carbon-rich asteroid, so the samples might resemble carbon-rich meteorites that have fallen to Earth, Thompson says. The bits collected by OSIRIS-REx probably contain organic compounds — carbon-based molecules found in many meteorites that are the building blocks of many exciting types of chemistry, including those conducive to life. “What I find most fascinating are the nucleobases, the components of the genetic code that make up all life from DNA and RNA,” says Daniel Glavin, the senior scientist for sample return at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Maryland. These compounds have been found in meteorites before, but those rocks have not been as pristine as the Bennu samples are expected to be. “We can trust the results, because this stuff is clean,” he says.
NASA curators will work their way through unpacking and studying the dust and pebbles inside OSIRIS-REx’s storage container in the coming weeks. Using nitrogen-filled gloveboxes, technicians will analyse the samples with scanners and other instruments to discern how many rock types were collected, and they will record the samples’ colour, volume and porosity.
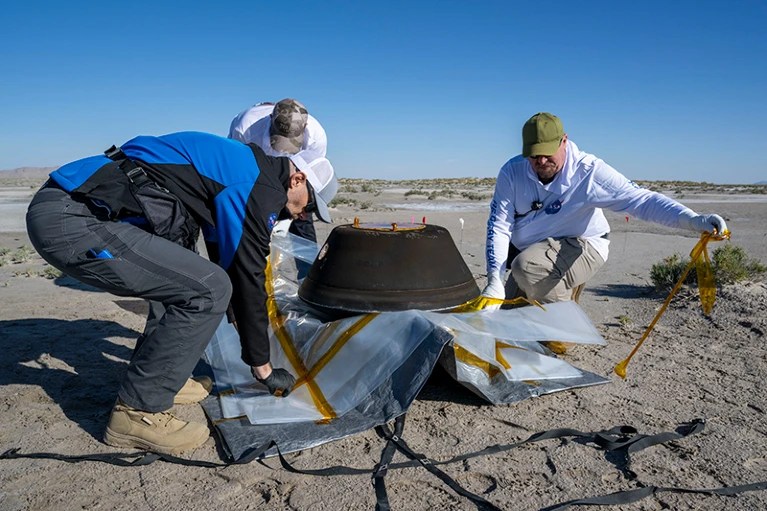
Mission specialists prepare the OSIRIS-REx sample capsule for transport to a clean room after its landing in the Utah desert on 24 September.Credit: Keegan Barber/NASA via Getty
The curators will collect up to 100 milligrams for the quick-look team to analyse over the first 72 hours. That initial sample will probably be made up of fine-grained material obtained from the outermost parts of the sample capsule, Thompson says. After that, the team will get a chance to study grains that were picked up by 24 stainless-steel contact pads on the outside of the sample container — which were the first things to actually come into contact with Bennu. It will probably be several weeks before the curators open the heart of the sample container and begin extracting the bulk of the material inside.
Early experiments could include looking at how material that was on the surface of Bennu compares with what came from deeper inside the asteroid, Thompson says. OSIRIS-REx’s robotic arm might have plunged as deep as 40 centimetres under Bennu’s rubbly surface when executing its fist bump.
Work interrupted?
NASA has scheduled a press conference on 11 October to unveil the first scientific results. But its work on the mission could be interrupted if the US government shuts down on 1 October. Republicans and Democrats in Congress have been battling over priorities for funding the federal government in 2024.
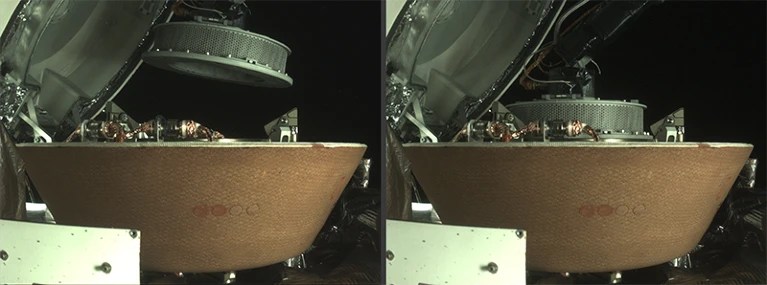
After OSIRIS-REx fist-bumped the asteroid Bennu in 2020, it pulled the collected samples into the spacecraft (left) and stowed them inside its sample-return capsule (right).Credit: NASA/Goddard/Univ. Arizona/Lockheed Martin
If the situation remains in a stalemate by the time the US fiscal year ends on 30 September, then federal agencies, including NASA, might close until an agreement can be reached. If that were to happen while the Bennu sample is at NASA, then “certain steps leading to its highly anticipated analysis will possibly be delayed, but the sample will remain protected and safe”, says Lori Glaze, head of NASA’s planetary sciences division. “The sample waited for more than 4 billion years for humans to study it, and if it takes us a little longer, I think we’ll be okay.”
At least 70% of the Bennu material will be saved for scientists outside NASA and for future generations to study. Furthermore, 4% of the sample will go to the Canadian Space Agency, which helped to build a laser instrument aboard OSIRIS-REx, and 0.5% will go to JAXA in exchange for samples of Ryugu, so that researchers can compare the two asteroids.
Meanwhile, the rest of the OSIRIS spacecraft continues to fly through space after dropping off its sample-return capsule. It is headed to study Apophis, an asteroid with a different, ‘stony’, chemical composition that will whizz dramatically close past Earth in 2029.
Copyright © 2023, Springer Nature Limited
ooOOoo
There we go, my credit to an incredible feat of exploration that, hopefully, will lead to some interesting results over the next few weeks.


Thank you for sharing Paul❣️
LikeLike
Val, a real pleasure to share. It is an amazing project, if that’s the right word.
LikeLiked by 1 person
It is truly amazing!
LikeLike
Thanks Val. As I said at the start of my post, “I just find this incredible”. Glad I was alive and reasonably fit, in the head, to appreciate what NASA and others did for the world.
LikeLiked by 1 person
A truly remarkable achievement!
LikeLike
John, you have described it perfectly!
LikeLike