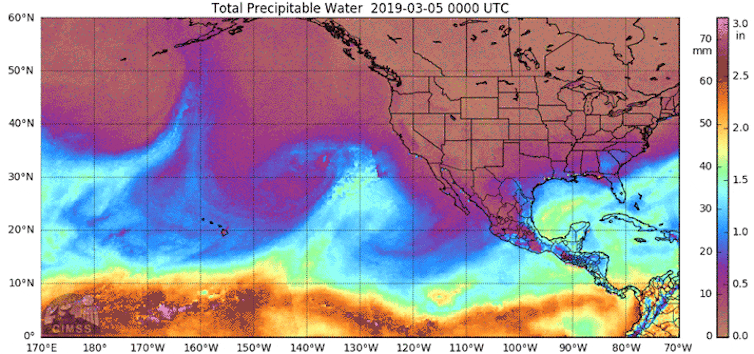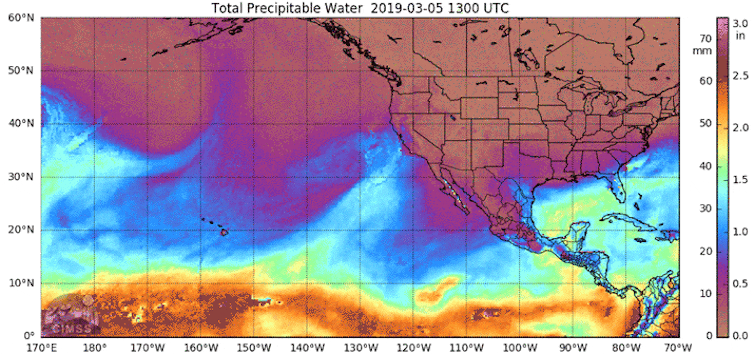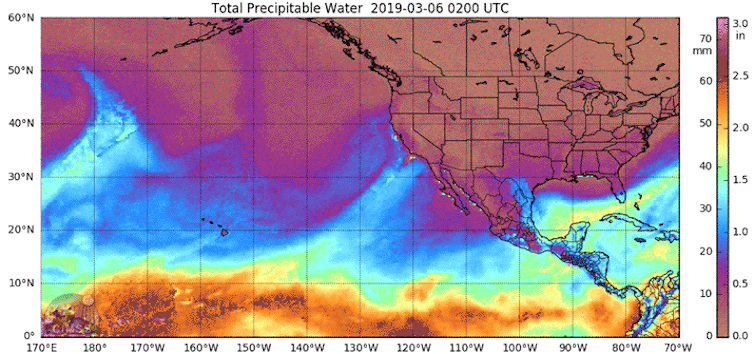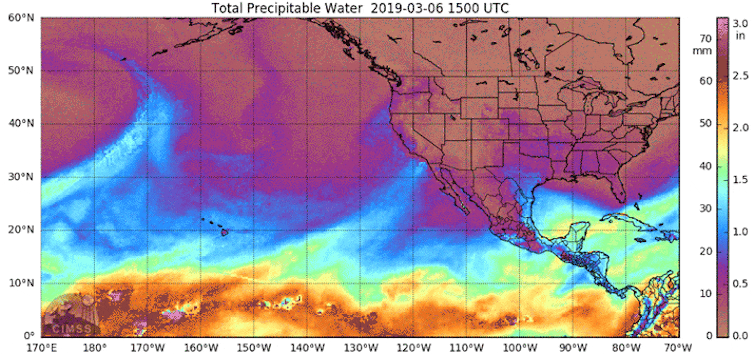
Returning to climate change.
We think that climate change is a relatively recent phenomenon. Wrong! And I am not going to say any more because this post from The Conversation covers it beautifully.
ooOOoo
What ancient farmers can really teach us about adapting to climate change – and how political power influences success or failure

Chelsea Fisher, University of South Carolina
Published February, 26th, 2024
In dozens of archaeological discoveries around the world, from the once-successful reservoirs and canals of Angkor Wat in Cambodia to the deserted Viking colonies of Greenland, new evidence paints pictures of civilizations struggling with unforeseen climate changes and the reality that their farming practices had become unsustainable.
Among these discoveries are also success stories, where ancient farming practices helped civilizations survive the hard times.
Zuni farmers in the southwestern United States made it through long stretches of extremely low rainfall between A.D. 1200 and 1400 by embracing small-scale, decentralized irrigation systems. Farmers in Ghana coped with severe droughts from 1450 to 1650 by planting indigenous African grains, like drought-tolerant pearl millet.
Ancient practices like these are gaining new interest today. As countries face unprecedented heat waves, storms and melting glaciers, some farmers and international development organizations are reaching deep into the agricultural archives to revive these ancient solutions.
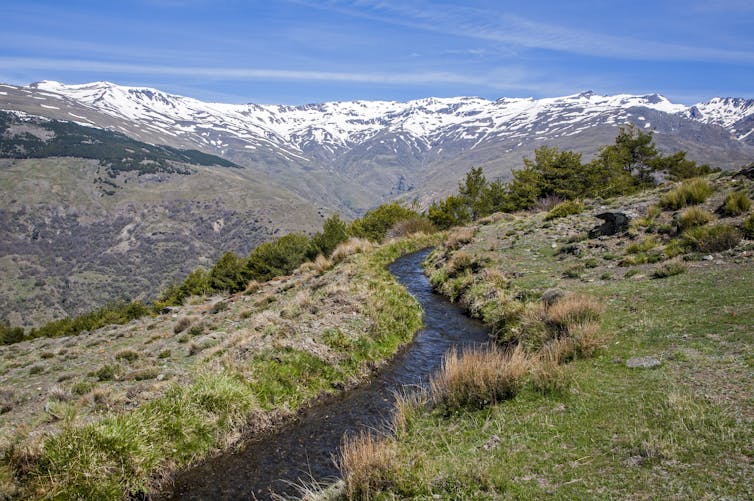

Drought-stricken farmers in Spain have reclaimed medieval Moorish irrigation technology. International companies hungry for carbon offsets have paid big money for biochar made using pre-Columbian Amazonian production techniques. Texas ranchers have turned to ancient cover cropping methods to buffer against unpredictable weather patterns.
But grasping for ancient technologies and techniques without paying attention to historical context misses one of the most important lessons ancient farmers can reveal: Agricultural sustainability is as much about power and sovereignty as it is about soil, water and crops.
I’m an archaeologist who studies agricultural sustainability in the past. Discoveries in recent years have shown how the human past is full of people who dealt with climate change in both sustainable and unsustainable ways. Archaeologists are finding that ancient sustainability was tethered closely to politics. However, these dynamics are often forgotten in discussions of sustainability today.
Maya milpa farming: Forest access is essential
In the tropical lowlands of Mexico and Central America, Indigenous Maya farmers have been practicing milpa agriculture for thousands of years. Milpa farmers adapted to drought by gently steering forest ecology through controlled burns and careful woodland conservation.
The knowledge of milpa farming empowered many rural farmers to navigate climate changes during the notorious Maya Collapse – two centuries of political disintegration and urban depopulation between A.D. 800 to 1000. Importantly, later Maya political leaders worked with farmers to keep this flexibility. Their light-handed approach is still legible in the artifacts and settlement patterns of post-Collapse farming communities and preserved in the flexible tribute schedules for Maya farmers documented by 16th century Spanish monks.
Maya farmers and researchers explain milpa farming.
In my book, “Rooting in a Useless Land: Ancient Farmers, Celebrity Chefs, and Environmental Justice in Yucatán,” I trace the deep history of the Maya milpa. Using archaeology, I show how ancient farmers adapted milpa agriculture in response to centuries of drought and political upheaval.
Modern Maya milpa practices began drawing public attention a few years ago as international development organizations partnered with celebrity chefs, like Noma’s René Redzepi, and embraced the concept.
However, these groups condemned the traditional milpa practice of burning new areas of forest as unsustainable. They instead promoted a “no-burn” version to grow certified organic maize for high-end restaurants. Their no-burn version of milpa relies on fertilizers to grow maize in a fixed location, rather than using controlled fire ecology to manage soil fertility across vast forests.
The result restricted the traditional practices Maya farmers have used for centuries. It also fed into a modern political threat to traditional Maya milpa farming: land grabs.
Traditional milpa agriculture requires a lot of forested land, since farmers need to relocate their fields every couple of years. But that need for forest is at odds with hotel companies, industrial cattle ranches and green energy developers who want cheap land and see Maya milpa forest management practices as inefficient. No-burn milpa eases this conflict by locking maize agriculture into one small space indefinitely, instead of spreading it out through the forest over generations. But it also changes tradition.
Maya milpa farmers are now fighting to practice their ancient agricultural techniques, not because they’ve forgotten or lost those techniques, but because neocolonial land privatization policies actively undermine farmers’ ability to manage woodlands as their ancestors did.
Milpa farmers are increasingly left to either adopt a rebranded version of their heritage or quit farming all together – as many have done.
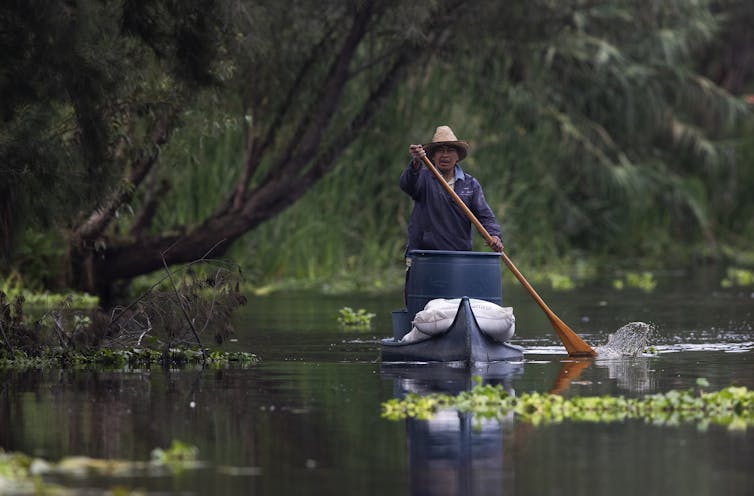
Mexico’s fragile artificial islands: Threats from development
When I look to the work of other archaeologists investigating ancient agricultural practices, I see these same entanglements of power and sustainability.
In central Mexico, chinampas are ancient systems of artificial islands and canals. They have enabled farmers to cultivate food in wetlands for centuries.
The continuing existence of chinampas is a legacy of deep ecological knowledge and a resource enabling communities to feed themselves.
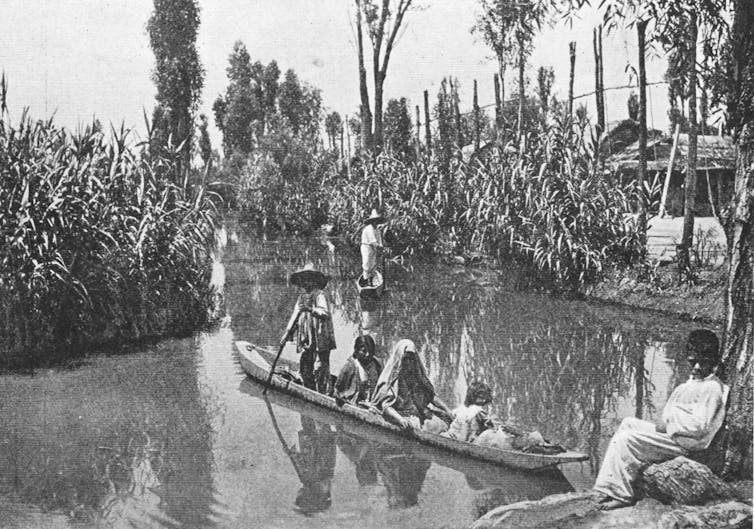
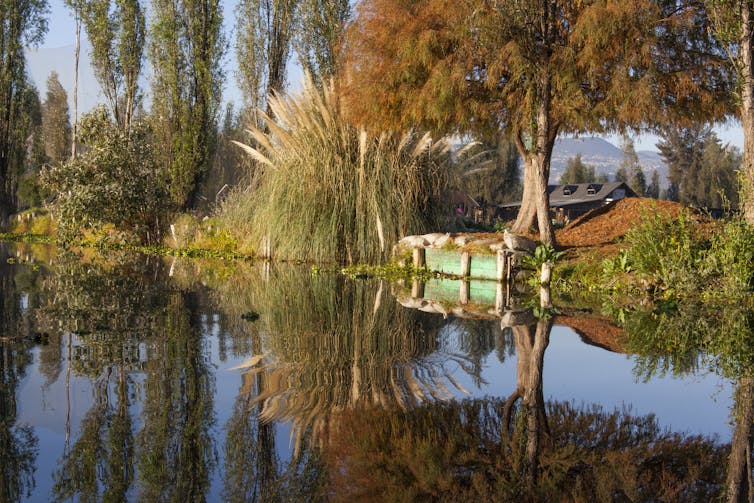


But archaeology has revealed that generations of sustainable chinampa management could be overturned almost overnight. That happened when the expansionist Aztec Empire decided to re-engineer Lake Xaltocan for salt production in the 14th century and rendered its chinampas unusable.
Today, the future of chinampa agriculture hinges on a pocket of protected fields stewarded by local farmers in the marshy outskirts of Mexico City. These fields are now at risk as demand for housing drives informal settlements into the chinampa zone.
Andean raised fields: A story of labor exploitation
Traditional Andean agriculture in South America incorporates a diverse range of ancient cultivation techniques. One in particular has a complicated history of attracting revival efforts.
In the 1980s, government agencies, archaeologists and development organizations spent a fortune trying to persuade Andean farmers to revive raised field farming. Ancient raised fields had been found around Lake Titicaca, on the border of Peru and Bolivia. These groups became convinced that this relic technology could curb hunger in the Andes by enabling back-to-back potato harvests with no need for fallowing.
But Andean farmers had no connection to the labor-intensive raised fields. The practice had been abandoned even before the rise of Inca civilization in the 13th century. The effort to revive ancient raised field agriculture collapsed.
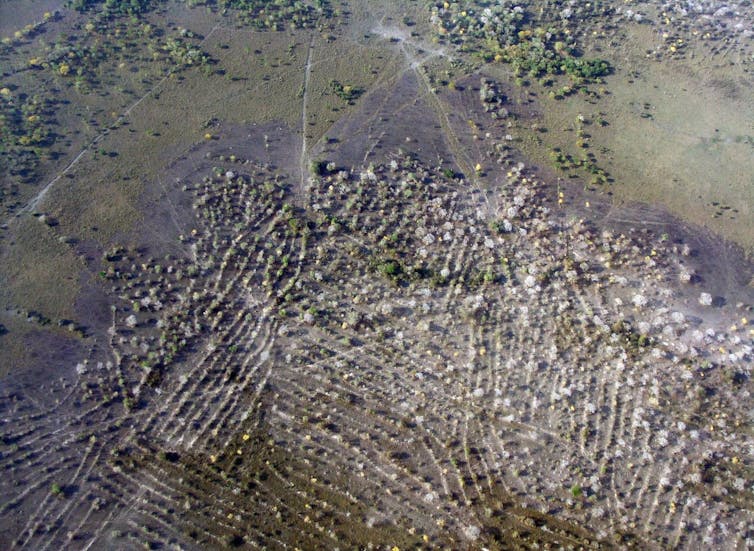

Since then, more archaeological discoveries around Lake Titicaca have suggested that ancient farmers were forced to work the raised fields by the expansionist Tiwanaku empire during its peak between AD 500 and 1100. Far from the politically neutral narrative promoted by development organizations, the raised fields were not there to help farmers feed themselves. They were a technology for exploiting labor and extracting surplus crops from ancient Andean farmers.
Respecting ancient practices’ histories
Reclaiming ancestral farming techniques can be a step toward sustainable food systems, especially when descendant communities lead their reclamation. The world can, and I think should, reach back to recover agricultural practices from our collective past.
But we can’t pretend that those practices are apolitical.
The Maya milpa farmers who continue to practice controlled burns in defiance of land privatizers understand the value of ancient techniques and the threat posed by political power. So do the Mexican chinampa farmers working to restore local food to disenfranchised urban communities. And so do the Andean farmers refusing to participate in once-exploitive raised field rehabilitation projects.
Depending on how they are used, ancient agricultural practices can either reinforce social inequalities or create more equitable food systems. Ancient practices aren’t inherently good – it takes a deeper commitment to just and equitable food systems to make them sustainable.
Chelsea Fisher, Assistant Professor of Anthropology, University of South Carolina
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
We like to think that the changing climate is a modern phenomenon but this article shows it is not. That sentence by Chelsea Fisher offers a route out of the present situation: “The world can, and I think should, reach back to recover agricultural practices from our collective past.”