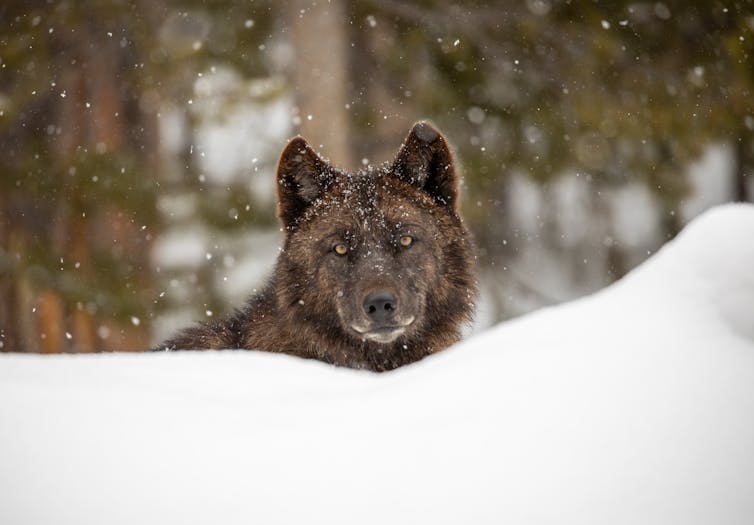
In this particular case looking at the wolf.
So many times a particular article from a website that allows republishing is not only a good and relevant article but also is a quick way of me publishing a post when, as I was yesterday, a bit pressed for time.
So here is that article from The Conversation.
ooOOoo
Wolf restoration in Colorado shows how humans are rethinking their relationships with wild animals

Christopher J. Preston, University of Montana
From sports to pop culture, there are few themes more appealing than a good comeback. They happen in nature, too. Even with the Earth losing species at a historic rate, some animals have defied the trend toward extinction and started refilling their old ecological niches.
I’m a philosopher based in Montana and specialize in environmental ethics. For my new book, “Tenacious Beasts: Wildlife Recoveries That Change How We Think About Animals,” I spent three years looking at wildlife comebacks across North America and Europe and considering the lessons they offer. In every case, whether the returnee is a bison, humpback whale, beaver, salmon, sea otter or wolf, the recovery has created an opportunity for humans to profoundly rethink how we live with these animals.
One place to see the rethink in action is Colorado, where voters approved a ballot measure in 2020 mandating the reintroduction of gray wolves west of the Continental Divide. Colorado’s Parks and Wildlife Agency has released a draft plan that calls for moving 30 to 50 gray wolves from other Rocky Mountain states into northwest Colorado over five years, starting in 2024.
Aldo Leopold, the famed conservationist and professor of game management at the University of Wisconsin, believed that moral beliefs evolve over time to become more inclusive of the natural world. And what’s happening in Colorado suggests Leopold was right. Human attitudes toward wolves have clearly evolved since the mid-1940s, when bounties, mass poisoning and trapping eradicated wolves from the state.
Recovering animals encounter a world that is markedly different from the one in which they declined, especially in terms of how people think about wildlife. Here are several reasons I see why societal attitudes toward wolves have changed. The importance of keystone species
Wolves released in northwest Colorado will wear GPS collars that enable wildlife managers to track them.
The idea that certain influential species, which ecologists call keystone species, can significantly alter the ecosystems around them first appeared in scientific literature in 1974. Bison, sea otters, beavers, elephants and wolves all exert this power. One way in which wolves wield influence is by preying on coyotes, which produces ripple effects across the system. Fewer coyotes means more rodents, which in turn means better hunting success for birds of prey.
Wolves also cause nervous behaviors among their prey. Some scientists believe that newly returned predators create a “landscape of fear” among prey species – a term that isn’t positive or negative, just descriptive. This idea has shifted thinking about predators. For example, elk avoid some areas when wolves are around, resulting in ecological changes that cascade down from the top. Vegetation can recover, which in turn may benefit other species.
Insights into pack dynamics
Animal behavioral science research has provided pointers for better wolf management. Studies show that wolf packs are less likely to prey on livestock if their social structure remains intact. This means that ranchers and wildlife managers should take care not to remove the pack’s breeding pair when problems occur. Doing so can fragment the pack and send dispersing wolves into new territories.
Wildlife agencies also have access to years of data from close observation of wolf behavior in places like Yellowstone National Park, where wolves were reintroduced starting in 1995. This research offers insights into the wolf’s intelligence and social complexity. All of this information helps to show how people can live successfully alongside them.
Predators provide economic value
Research has also demonstrated that wolves provide economic benefits to states and communities. Wisconsin researchers discovered that changes in deer behavior due to the presence of wolves have saved millions of dollars in avoided deer collisions with cars. These savings far exceed what it costs the state to manage wolves.
Wolf recovery has been shown to be a net economic benefit in areas of the U.S. West where they have returned. The dollars they attract from wolf-watchers, photographers and foreign visitors have provided a valuable new income stream in many communities.
Predators do kill livestock, but improved tracking has helped to put these losses in perspective. Montana Board of Livestock numbers show that wolves, grizzly bears and mountain lions caused the loss of 131 cattle and 137 sheep in the state in 2022. This is from a total of 2,200,000 cattle and 190,000 sheep. Of the 131 cattle, 36 were confirmed to be taken by wolves – 0.0016% of the statewide herd.
According to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, dogs, foxes and coyotes in Montana all killed more sheep and lambs than wolves did in 2020. Even eagles were three times more deadly to sheep and lambs than wolves were.
Actual costs to ranchers are certainly higher than these numbers suggest. The presence of wolves causes livestock to lose weight because the animals feed more nervously when wolves are around. Ranchers also lose sleep as they worry about wolves attacking their livestock and guard dogs. And clearly, low statewide kills are small comfort to a rancher who loses a dozen or more animals in one year. Margins are always tight in the livestock business.
t
A northern Colorado rancher discusses options for protecting his cattle from wolves, which already are naturally present in the state.
What’s more, predators’ economic impacts don’t end with ranching. In Colorado, for example, elk numbers are likely to decline after wolves are reintroduced. This may affect state wildlife agency budgets that rely on license fees from elk hunters. It may also affect hunting outfitters’ incomes.
In my view, voters who supported bringing wolves back to Colorado should remain deeply aware of the full distribution of costs and support proactive compensation schemes for losses. They should be mindful that support for wolf reintroduction varies drastically between urban and rural communities and should insist that effective mechanisms are in place ahead of time to ensure fair sharing of the economic burdens that wolves generate.
A new ethical playing field
Despite these complexities, the idea of the “big bad wolf” clearly no longer dominates Americans’ thinking. And the wolf is not alone. Social acceptance of many other wildlife species is also increasing. For example, a 2023 study found that between 80% and 90% of Montanans believed grizzly bears – which are recovering and expanding their presence there – have a right to exist.
Aldo Leopold famously claimed to have experienced an epiphany when he shot a wolf in New Mexico in the 1920s and saw “a fierce green fire” dying in her eyes. In reality, his attitude took several more decades to change. Humans may have an ingrained evolutionary disposition to fear carnivorous predators like wolves, but the change ended up being real for Leopold, and it lasted.
Leopold, who died in 1948, did not live to see many wildlife species recover, but I believe he would have regarded what’s happening now as an opportunity for Americans’ moral growth. Because Leopold knew that ethics, like animals, are always evolving.
Christopher J. Preston, Professor of Philosophy, University of Montana
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
Those last few paragraphs under the sub-heading of ‘A new ethical playing field’ show how many other wildlife species have gained a real advantage, a social acceptance as the article said. Long may it continue.