A return to Unsplash. (And this time not dogs!)
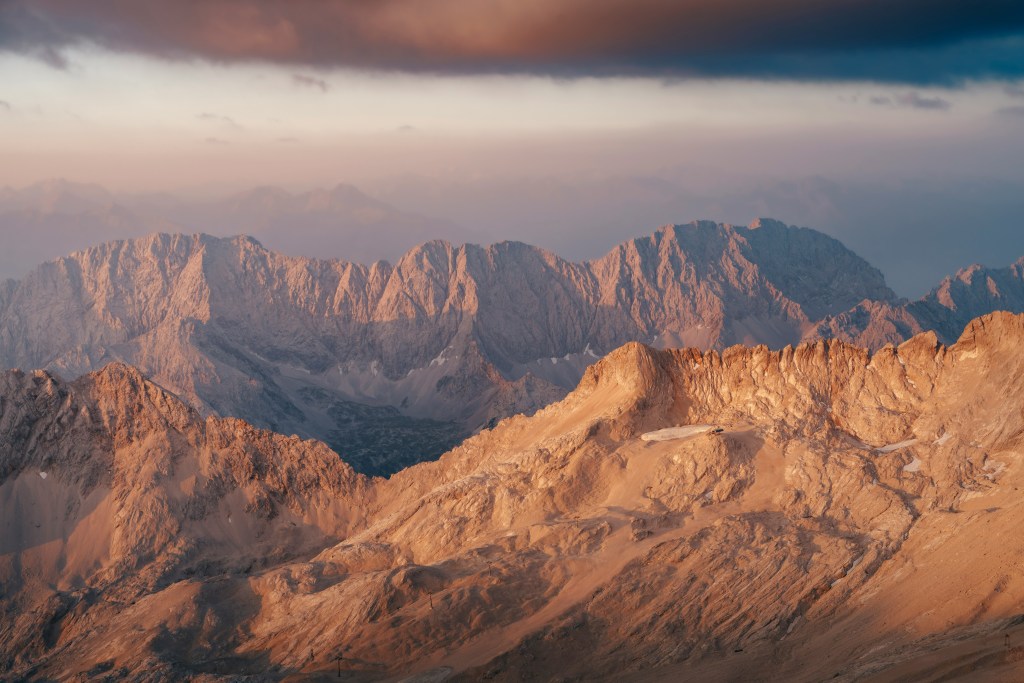
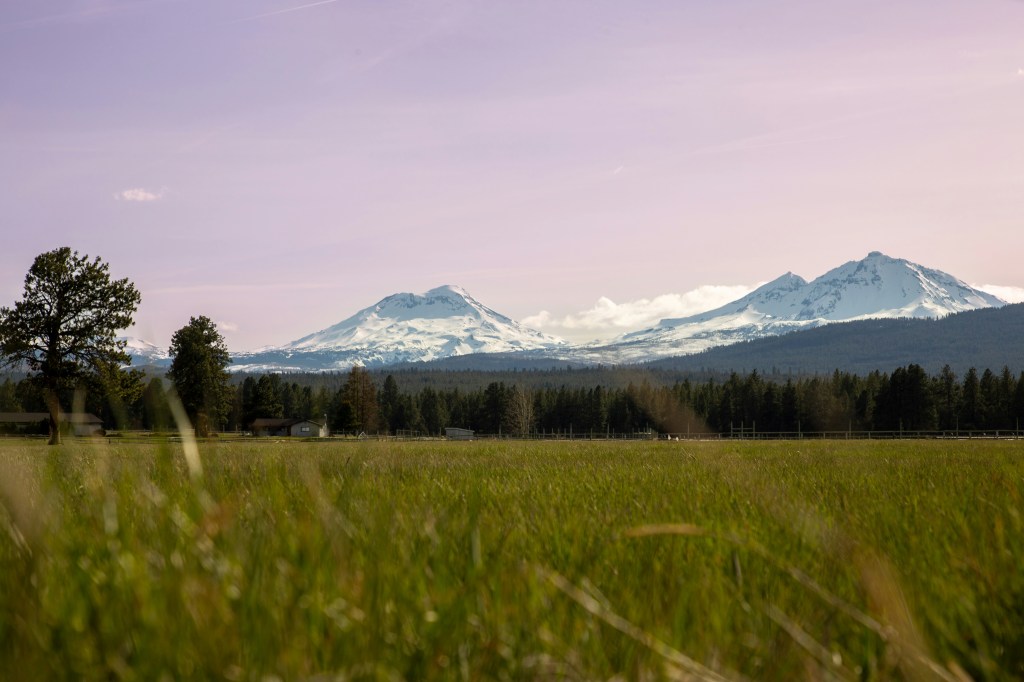
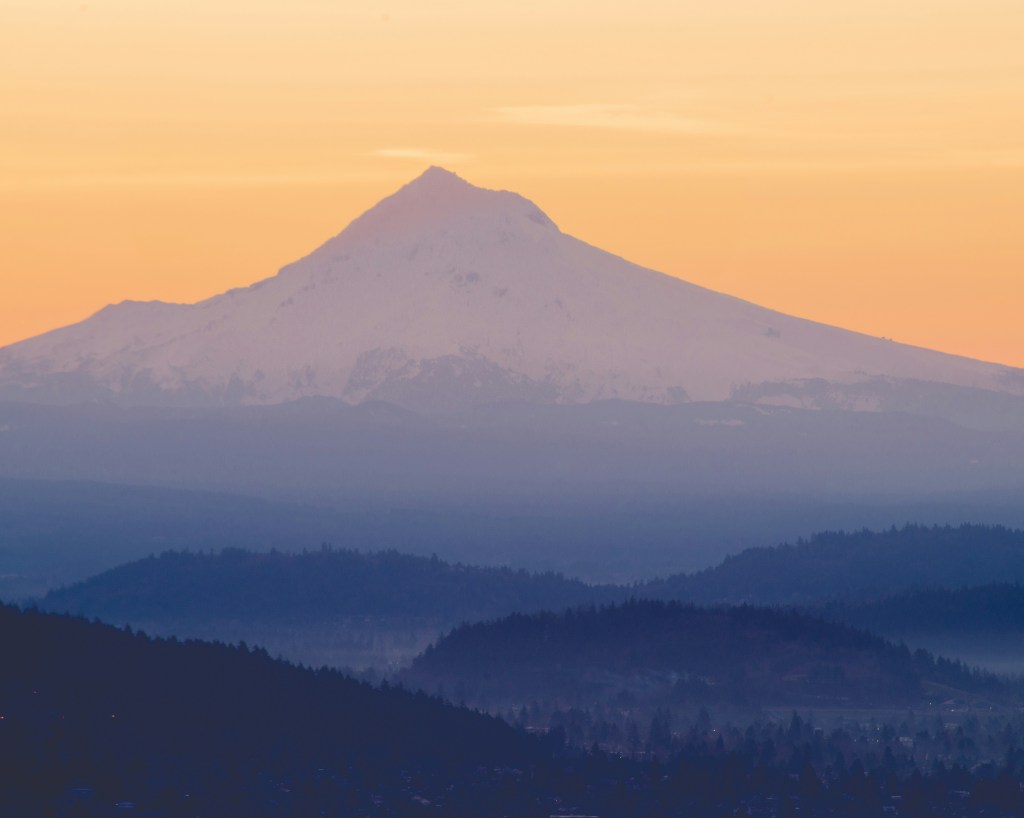
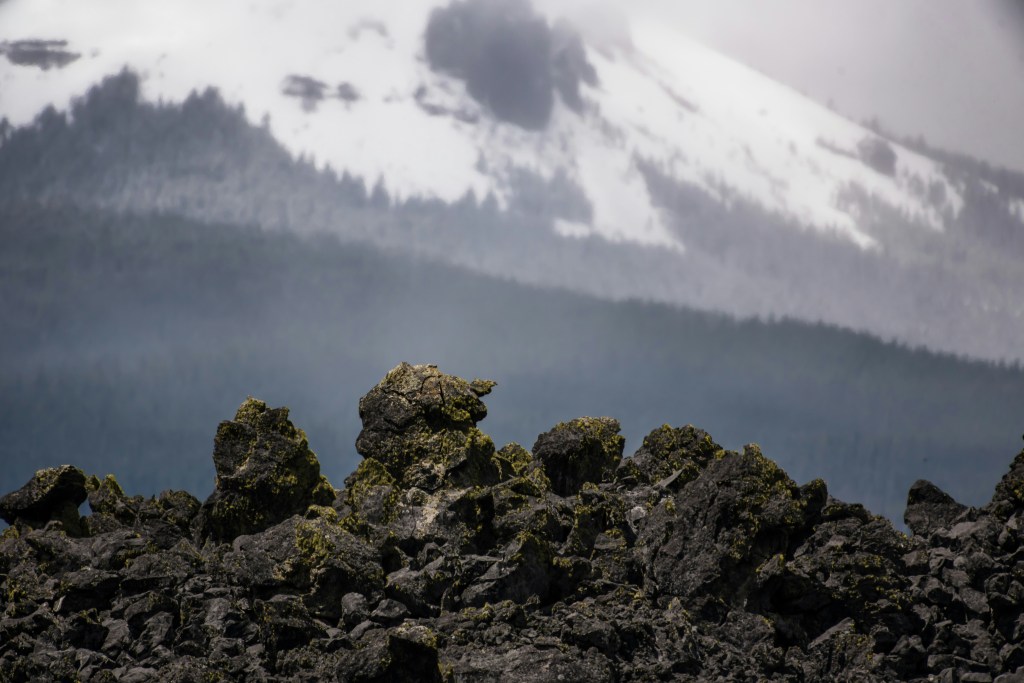
Oregon Landscapes

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo
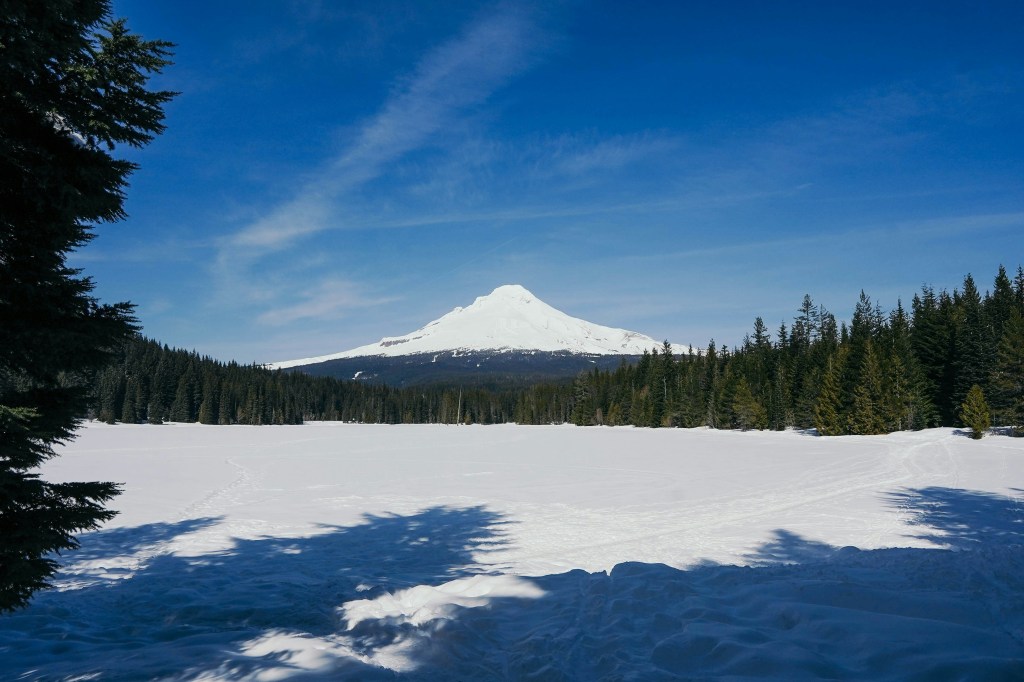

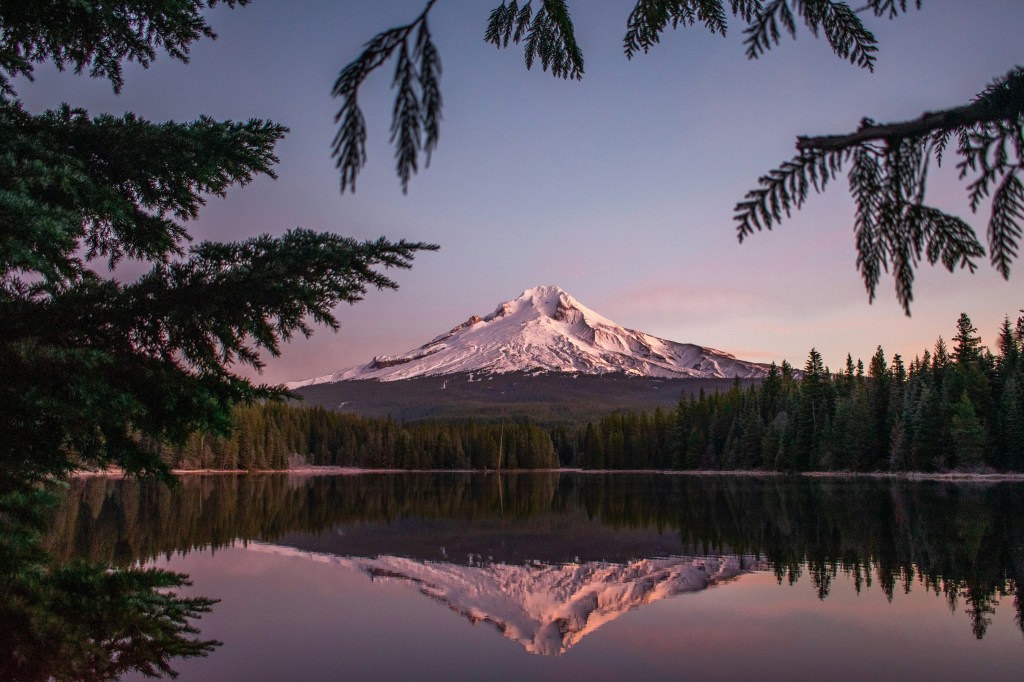
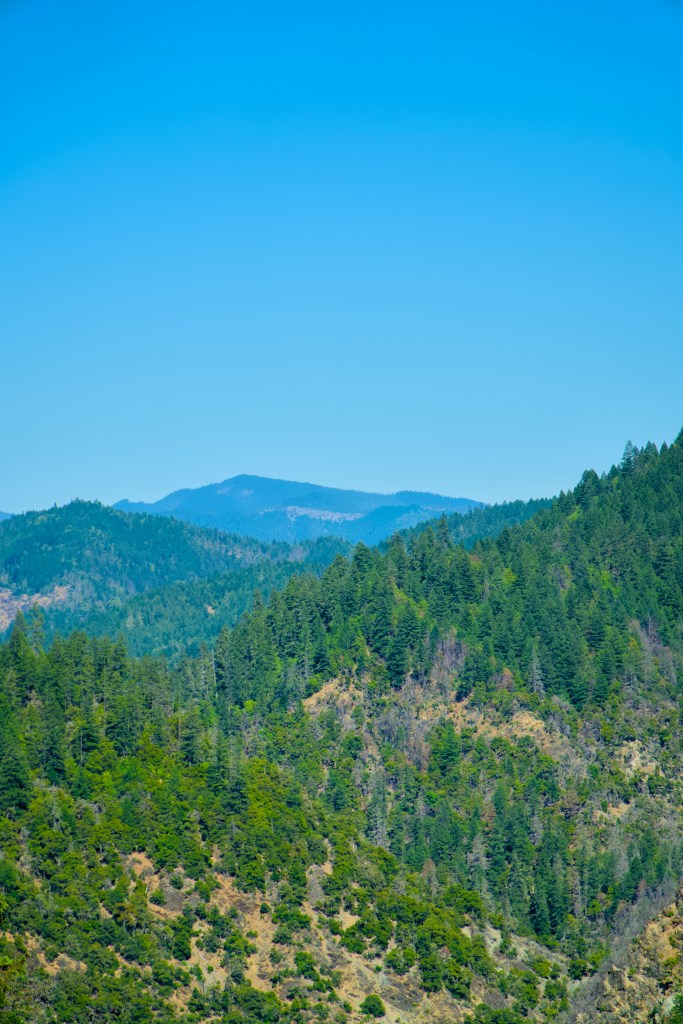
These are mainly mountain views but endorse the beauty of the State of Oregon.
Dogs are animals of integrity. We have much to learn from them.
A return to Unsplash. (And this time not dogs!)
Oregon Landscapes

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

These are mainly mountain views but endorse the beauty of the State of Oregon.
A fascinating article from The Conversation.
ooOOoo

Juliette Becker, University of Wisconsin-Madison
The Sun will someday die. This will happen when it runs out of hydrogen fuel in its core and can no longer produce energy through nuclear fusion as it does now. The death of the Sun is often thought of as the end of the solar system. But in reality, it may be the beginning of a new phase of life for all the objects living in the solar system.
When stars like the Sun die, they go through a phase of rapid expansion called the Red Giant phase: The radius of the star gets bigger, and its color gets redder. Once the gravity on the star’s surface is no longer strong enough for it to hold on to its outer layers, a large fraction – up to about half – of its mass escapes into space, leaving behind a remnant called a white dwarf.
I am a professor of astronomy at the University of Wisconsin-Madison. In 2020, my colleagues and I discovered the first intact planet orbiting around a white dwarf. Since then, I’ve been fascinated by the prospect of life on planets around these, tiny, dense white dwarfs.
Researchers search for signs of life in the universe by waiting until a planet passes between a star and their telescope’s line of sight. With light from the star illuminating the planet from behind, they can use some simple physics principles to determine the types of molecules present in the planet’s atmosphere.
In 2020, researchers realized they could use this technique for planets orbiting white dwarfs. If such a planet had molecules created by living organisms in its atmosphere, the James Webb Space Telescope would probably be able to spot them when the planet passed in front of its star.
In June 2025, I published a paper answering a question that first started bothering me in 2021: Could an ocean – likely needed to sustain life – even survive on a planet orbiting close to a dead star?
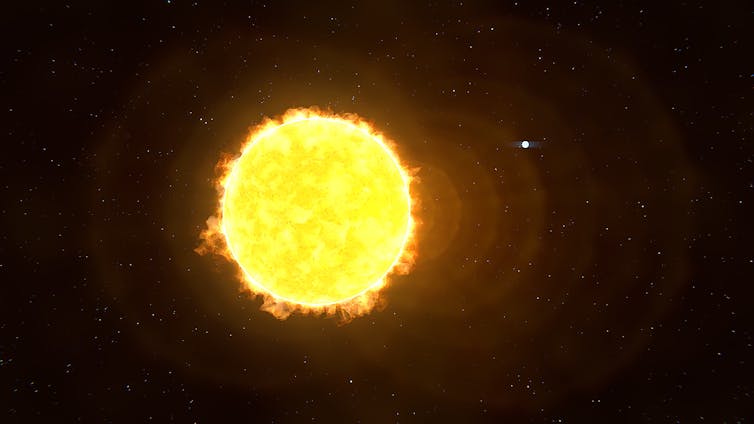

A white dwarf has about half the mass of the Sun, but that mass is compressed into a volume roughly the size of Earth, with its electrons pressed as close together as the laws of physics will allow. The Sun has a radius 109 times the size of Earth’s – this size difference means that an Earth-like planet orbiting a white dwarf could be about the same size as the star itself.
White dwarfs are extremely common: An estimated 10 billion of them exist in our galaxy. And since every low-mass star is destined to eventually become a white dwarf, countless more have yet to form. If it turns out that life can exist on planets orbiting white dwarfs, these stellar remnants could become promising and plentiful targets in the search for life beyond Earth.
But can life even exist on a planet orbiting a white dwarf? Astronomers have known since 2011 that the habitable zone is extremely close to the white dwarf. This zone is the location in a planetary system where liquid water could exist on a planet’s surface. It can’t be too close to the star that the water would boil, nor so far away that it would freeze.
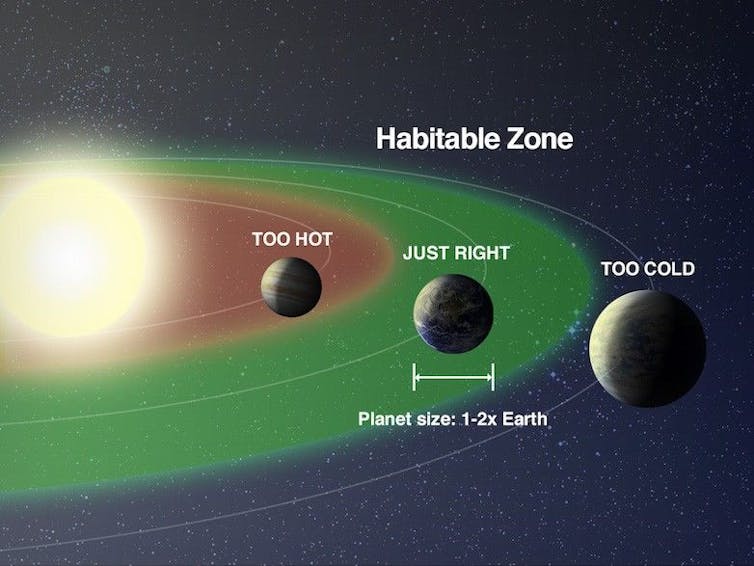
The habitable zone around a white dwarf would be 10 to 100 times closer to the white dwarf than our own habitable zone is to our Sun, since white dwarfs are so much fainter.
Being so close to the surface of the white dwarf would bring new challenges to emerging life that more distant planets, like Earth, do not face. One of these is tidal heating.
Tidal forces – the differences in gravitational forces that objects in space exert on different parts of a nearby second object – deform a planet, and the friction causes the material being deformed to heat up. An example of this can be seen on Jupiter’s moon Io.
The forces of gravity exerted by Jupiter’s other moons tug on Io’s orbit, deforming its interior and heating it up, resulting in hundreds of volcanoes erupting constantly across its surface. As a result, no surface water can exist on Io because its surface is too hot.
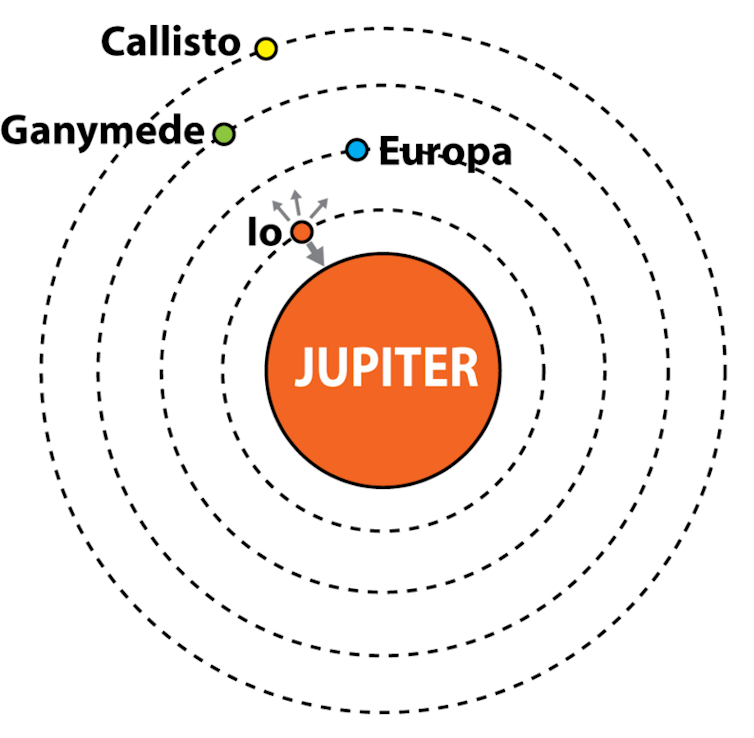
In contrast, the adjacent moon Europa is also subject to tidal heating, but to a lesser degree, since it’s farther from Jupiter. The heat generated from tidal forces has caused Europa’s ice shell to partially melt, resulting in a subsurface ocean.
Planets in the habitable zone of a white dwarf would have orbits close enough to the star to experience tidal heating, similar to how Io and Europa are heated from their proximity to Jupiter.
This proximity itself can pose a challenge to habitability. If a system has more than one planet, tidal forces from nearby planets could cause the planet’s atmosphere to trap heat until it becomes hotter and hotter, making the planet too hot to have liquid water.
Even if there is only one planet in the system, it may not retain its water.
In the process of becoming a white dwarf, a star will expand to 10 to 100 times its original radius during the red giant phase. During that time, anything within that expanded radius will be engulfed and destroyed. In our own solar system, Mercury, Venus and Earth will be destroyed when the Sun eventually becomes a red giant before transitioning into a white dwarf.
For a planet to survive this process, it would have to start out much farther from the star — perhaps at the distance of Jupiter or even beyond.
If a planet starts out that far away, it would need to migrate inward after the white dwarf has formed in order to become habitable. Computer simulations show that this kind of migration is possible, but the process could cause extreme tidal heating that may boil off surface water – similar to how tidal heating causes Io’s volcanism. If the migration generates enough heat, then the planet could lose all its surface water by the time it finally reaches a habitable orbit.
However, if the migration occurs late enough in the white dwarf’s lifetime – after it has cooled and is no longer a hot, bright, newly formed white dwarf – then surface water may not evaporate away.
Under the right conditions, planets orbiting white dwarfs could sustain liquid water and potentially support life.
Astronomers haven’t yet found any Earth-like, habitable exoplanets around white dwarfs. But these planets are difficult to detect.
Traditional detection methods like the transit technique are less effective because white dwarfs are much smaller than typical planet-hosting stars. In the transit technique, astronomers watch for the dips in light that occur when a planet passes in front of its host star from our line of sight. Because white dwarfs are so small, you would have to be very lucky to see a planet passing in front of one.
The transit technique for detecting exoplanets requires watching for the dip in brightness when a planet passes in front of its host star.
Nevertheless, researchers are exploring new strategies to detect and characterize these elusive worlds using advanced telescopes such as the Webb telescope.
If habitable planets are found to exist around white dwarfs, it would significantly broaden the range of environments where life might persist, demonstrating that planetary systems may remain viable hosts for life even long after the death of their host star.
Juliette Becker, Assistant Professor of Astronomy, University of Wisconsin-Madison
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
I take my hats off to the researchers that are looking for life elsewhere.
The loss of an icon.
Firstly, from the BBC News website.
Graham Greene, the Canadian First Nations actor who starred in films including Dances With Wolves, has died aged 73, his manager says.
“It is with deep sadness we announce the peaceful passing of award-winning legendary Canadian actor Graham Greene,” Gerry Jordan said in a statement to CBC News. The outlet reported he died of natural causes.
Greene scored an Academy Award nomination for Best Supporting Actor for his role in Kevin Costner’s 1990 epic western, where he played Kicking Bird.
He was a member of the Oneida Nation, part of the Six Nations Reserve in southern Ontario.
Greene worked as a draftsman, civil technologist, steelworker and rock-band crew member before starting his career in theatre in the UK in the 1970s.
In a 2012 interview with Canadian publication Playback, he credited theatre with giving him a grounding for acting.
“It helps you build a character. When you get into film you don’t have that luxury. The discipline of theatre is what I recommend to all actors.”
In the same interview, he said a key moment for him came when he married his wife Hilary Blackmore, which led to “the best time of my life”.
His breakthrough came in 1990 when he played Kicking Bird, a Lakota medicine man, in Dances With Wolves. Greene won widespread acclaim for the role.
He also appeared in the 1992 western thriller Thunderheart, playing tribal officer Walter Crow Horse.
In the 1999 fantasy drama The Green Mile, Greene played Arlen Bitterbuck, a Native American man on death row in prison.
He also starred in Die Hard With A Vengeance (1995), Maverick (1994), The Twilight Saga: New Moon (2009) and Wind River (2017).
He picked up numerous awards through his storied career, including the Earle Grey Award for Lifetime Achievement by the Academy of Canadian Film and Television in 2004.
In 2016, he was inducted into the Order of Canada, the country’s second highest civilian honour.
Second, the YouTube dedication to Graham Greene.
Please watch the video.
Graham Greene will be missed; big time!
The Silent Global Emergency.
First, let me go to the Skeptic website where more details are explained.
Today on the podcast, economist Dean Spears explains the forces driving global population change, from past fears of overpopulation to today’s concerns about declining birth rates.
He contrasts the perspectives of biologists and economists on population growth and highlights the role of human ideas and innovation in sustaining progress. Spears also discusses misconceptions about zero-sum economics, the links between population, health, and economic well-being, and the rise of anti-natalism.
The conversation covers population size and environmental concerns, government policies on family planning, and why cultural attitudes toward reproduction may be as important as policy in addressing the challenges of a shrinking population.
Dean Spears is an economist, demographer, and associate professor at the University of Texas.
His talk is available on YouTube. It is not a short talk, about an hour and a quarter, but it is incredibly interesting.
I’m speaking of a series on BBC Radio 4.
The series is called Naturebang: “Becky Ripley and Emily Knight make sense of what it means to be human by looking to the natural world… Science meets storytelling with a philosophical twist.“
The website is: https://www.bbc.co.uk/programmes/m00060x0
There are 35 episodes. I particularly liked the episode broadcast yesterday about the Clams.
“How do we extract the maximum amount of power from the sun? Becky Ripley and Emily Knight enlist the help of a giant, thousand-year old clam. And end up in the depths of space…
Featuring Professor Alison Sweeney at Yale University, and Mike Garrett from the Jodrell Bank Centre for Astrophysics.
Produced and presented by Emily Knight and Becky Ripley“
Amazing!

oooo
oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

oooo

There are few people visiting Learning from Dogs these days but so what! I do not publish posts to elicit comments or ‘Likes’, I just do it for my own pleasure, and if there are a very few who like my blog posts then that is a bonus.
Plus I cannot guarantee that some of these photographs have not appeared in earlier Picture Parades.
Came across this a few days ago and you will love it!
The new world comes up with some marvellous treats. Here I was listening to the radio (BBC – Radio 4) from Southern Oregon and they had this item about a Scottish thatcher using a variety of plants to thatch roofs. The thatcher had been thatching for years.
Then a quick search on the internet found this video:
Far too short!
However really enjoyed the video.
An interesting article about the benefits of being active.
I try and stay as active as I can mainly by bicycle riding. This article from The Conversation shows the importance of this. It is just a shame that they do not mention being old and active; as in being 80!
ooOOoo
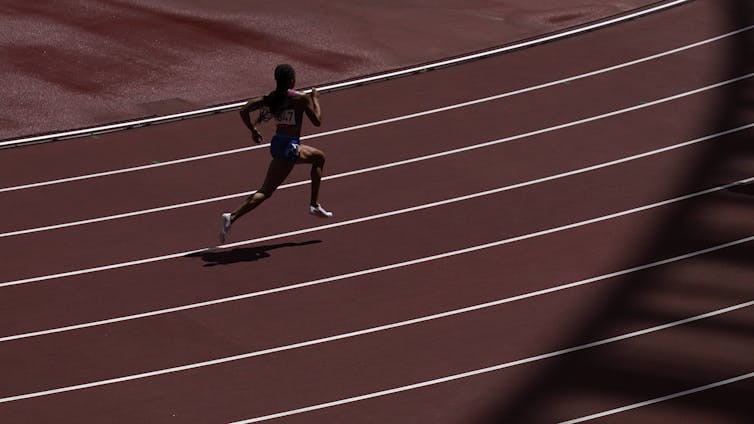

Fiddy Davis Jaihind Jothikaran, Hope College
In a world where sports are dominated by youth and speed, some athletes in their late 30s and even 40s are not just keeping up – they are thriving.
Novak Djokovic is still outlasting opponents nearly half his age on tennis’s biggest stages. LeBron James continues to dictate the pace of NBA games, defending centers and orchestrating plays like a point guard. Allyson Felix won her 11th Olympic medal in track and field at age 35. And Tom Brady won a Super Bowl at 43, long after most NFL quarterbacks retire.
The sustained excellence of these athletes is not just due to talent or grit – it’s biology in action. Staying at the top of their game reflects a trainable convergence of brain, body and mindset. I’m a performance scientist and a physical therapist who has spent over two decades studying how athletes train, taper, recover and stay sharp. These insights aren’t just for high-level athletes – they hold true for anyone navigating big life changes or working to stay healthy.
Increasingly, research shows that the systems that support high performance – from motor control to stress regulation, to recovery – are not fixed traits but trainable capacities. In a world of accelerating change and disruption, the ability to adapt to new changes may be the most important skill of all. So, what makes this adaptability possible – biologically, cognitively and emotionally?
Neuroscience research shows that with repeated exposure to high-stakes situations, the brain begins to adapt. The prefrontal cortex – the region most responsible for planning, focus and decision-making – becomes more efficient in managing attention and making decisions, even under pressure.
During stressful situations, such as facing match point in a Grand Slam final, this area of the brain can help an athlete stay composed and make smart choices – but only if it’s well trained.
In contrast, the amygdala, our brain’s threat detector, can hijack performance by triggering panic, freezing motor responses or fueling reckless decisions. With repeated exposure to high-stakes moments, elite athletes gradually reshape this brain circuit.
They learn to tune down amygdala reactivity and keep the prefrontal cortex online, even when the pressure spikes. This refined brain circuitry enables experienced performers to maintain their emotional control.
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor, or BDNF, is a molecule that supports adapting to changes quickly. Think of it as fertilizer for the brain. It enhances neuroplasticity: the brain’s ability to rewire itself through experience and repetition. This rewiring helps athletes build and reinforce the patterns of connections between brain cells to control their emotion, manage their attention and move with precision.
BDNF levels increase with intense physical activity, mental focus and deliberate practice, especially when combined with recovery strategies such as sleep and deep breathing.
Elevated BDNF levels are linked to better resilience against stress and may support faster motor learning, which is the process of developing or refining movement patterns.
For example, after losing a set, Djokovic often resets by taking deep, slow breaths – not just to calm his nerves, but to pause and regain control. This conscious breathing helps him restore focus and likely quiets the stress signals in his brain.
In moments like these, higher BDNF availability likely allows him to regulate his emotions and recalibrate his motor response, helping him to return to peak performance faster than his opponent.
In essence, athletes who repeatedly train and compete in pressure-filled environments are rewiring their brain to respond more effectively to those demands. This rewiring, from repeated exposures, helps boost BDNF levels and in turn keeps the prefrontal cortex sharp and dials down the amygdala’s tendency to overreact.
This kind of biological tuning is what scientists call cognitive reserve and allostasis – the process the body uses to make changes in response to stress or environmental demands to remain stable. It helps the brain and body be flexible, not fragile.
Importantly, this adaptation isn’t exclusive to elite athletes. Studies on adults of all ages show that regular physical activity – particularly exercises that challenge both body and mind – can raise BDNF levels, improve the brain’s ability to adapt and respond to new challenges, and reduce stress reactivity.
Programs that combine aerobic movement with coordination tasks, such as dancing, complex drills or even fast-paced walking while problem-solving have been shown to preserve skills such as focus, planning, impulse control and emotional regulation over time.
After an intense training session or a match, you will often see athletes hopping on a bike or spending some time in the pool. These low-impact, gentle movements, known as active recovery, help tone down the nervous system gradually.
Outside of active recovery, sleep is where the real reset and repair happen. Sleep aids in learning and strengthens the neural connections challenged during training and competition.

Over time, this convergence creates a trainable loop between the brain and body that is better equipped to adapt, recover and perform.
While the spotlight may shine on sporting arenas, you don’t need to be a pro athlete to train these same skills.
The ability to perform under pressure is a result of continuing adaptation. Whether you’re navigating a career pivot, caring for family members, or simply striving to stay mentally sharp as the world changes, the principles are the same: Expose yourself to challenges, regulate stress and recover deliberately.
While speed, agility and power may decline with age, some sport-specific skills such as anticipation, decision-making and strategic awareness actually improve. Athletes with years of experience develop faster mental models of how a play will unfold, which allows them to make better and faster choices with minimal effort. This efficiency is a result of years of reinforcing neural circuits that doesn’t immediately vanish with age. This is one reason experienced athletes often excel even if they are well past their physical prime.
Physical activity, especially dynamic and coordinated movement, boosts the brain’s capacity to adapt. So does learning new skills, practicing mindfulness and even rehearsing performance under pressure. In daily life, this might be a surgeon practicing a critical procedure in simulation, a teacher preparing for a tricky parent meeting, or a speaker practicing a high-stakes presentation to stay calm and composed when it counts. These aren’t elite rituals – they’re accessible strategies for building resilience, motor efficiency and emotional control.
Humans are built to adapt – with the right strategies, you can sustain excellence at any stage of life.
Fiddy Davis Jaihind Jothikaran, Associate Professor of Kinesiology, Hope College
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
… “you can sustain excellence at any stage of life.” Even at 80 years old? 😉
It is 30 minutes long but it is incredibly important!
Heather Richardson writes the blog Letters from an American.
On August 14th Heather recorded a live interview with California Governor Gavin Newsom.
Watch it!