And it isn’t all that one might expect!
Jeannie and I are at opposite ends of the scale, so to speak. The older I get the more I want everything in the same place, primarily because I cannot remember where I previously put something.
Jeannie loves putting stuff anywhere because she can recall where it is!
So an article in The Conversation was fascinating.
ooOOoo
Decluttering can be stressful − a clinical psychologist explains how personal values can make it easier

Mary E. Dozier, Mississippi State University
I recently helped my mom sort through boxes she inherited when my grandparents passed away. One box was labeled – either ironically or genuinely – “toothpick holders and other treasures.” Inside were many keepsakes from moments now lost to history – although we found no toothpick holders.
My favorite of the items we sorted through was a solitary puzzle piece, an artifact reflecting my late grandmother’s penchant for hiding the final piece to a jigsaw puzzle just to swoop in at the last moment and finish it.
After several hours of reminiscing, my mom and I threw away 90% of what we had sorted.
“Why did I keep this?” is a question I hear frequently, both from my family and friends and from patients. I am a licensed clinical psychologist whose research focuses on the characterization, assessment and treatment of hoarding disorder, particularly for adults 60 years of age or older. As such, I spend a great deal of my time thinking about this question.
What drives the need to keep stuff?
Hoarding disorder is a psychiatric condition defined by urges to save items and difficulty discarding current possessions. For adults with “clinically severe” hoarding disorder, this leads to a level of household clutter that impairs daily functioning and can even create a fire hazard. In my professional experience, however, many adults struggle with clutter even if they do not meet the clinical criteria for hoarding disorder.
Holding on to things that have sentimental value or could be useful in the future is a natural part of growing older. For some people, though, this tendency to hold on to objects grows over time, to the point that they eventually do meet criteria for hoarding disorder. Age-related changes in executive function may help explain the increase in prevalence of hoarding disorder as we get older; increasing difficulty with decision-making in general also affects decisions around household clutter.
The traditional model behind hoarding disorder suggests that difficulty with discarding comes from distress during decision-making. However, my research shows that this may be less true of older adults.
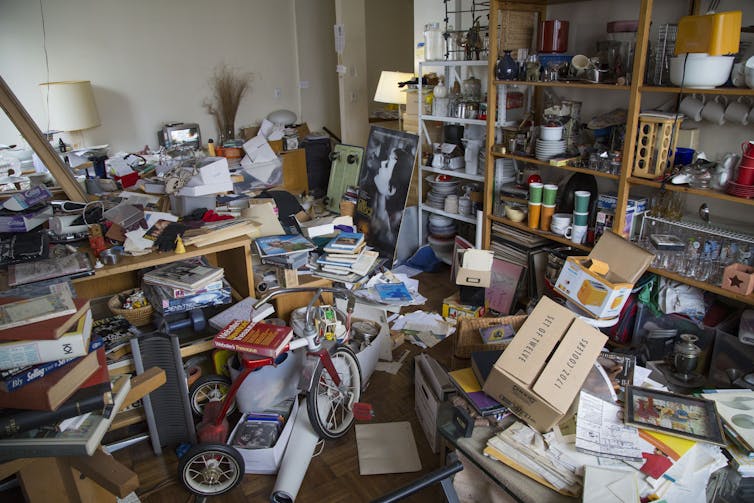

When I was a graduate student, I conducted a study in which we asked adults with hoarding disorder to spend 15 minutes making decisions about whether to keep or discard various items brought from their home. Participants could sort whatever items they wanted. Most chose to sort paper items such as old mail, cards or notes.
We found that age was associated with lower levels of distress during the task, such that participants who were older tended to feel less stressed when making the decision about what to keep and what to discard. We also found that many participants, particularly those who were older, actually reported positive emotions while sorting their items.
In new research publishing soon, my current team replicated this finding using a home-based version of the task. This suggests that fear of making the wrong decision isn’t a universal driver of our urge to save items.
In fact, a study my team published in August 2024 with adults over 50 with hoarding disorder suggests that altruism, a personality trait of wanting to help others, may explain why some people keep items that others might discard. My colleagues and I compared our participants’ personality profiles with that of adults in the general population of the same gender and age group. Compared with the general population, participants with hoarding disorder scored almost universally high on altruism.
Altruism also comes up frequently in my clinical work with older adults who struggle with clutter. People in our studies often tell me that they have held onto something out of a sense of responsibility, either for the item itself or to the environment.
“I need it to go to a good home” and “my grandmother gave this to me” are sentiments we commonly hear. Thus, people may keep things not out of fear of losing them but because saving them is consistent with their values. https://www.youtube.com/embed/JNVjPM1cIbg?wmode=transparent&start=0 Your values can help guide which possessions should stay in your life and which ones should go.
Leaning into values
In a 2024 study, my team demonstrated that taking a values-based approach to decluttering helps older adults to decrease household clutter and increases their positive affect, a state of mind characterized by feelings such as joy and contentment. Clinicians visited the homes of older adults with hoarding disorder for one hour per week for six weeks. At each visit, the clinicians used a technique called motivational interviewing to help participants talk through their decisions while they sorted household clutter.
We found that having participants start with identifying their values allowed them to maintain focus on their long-term goals. Too often, people focus on the immediate ability of an object to “spark joy” and forget to consider whether an object has greater meaning and purpose. Values are the abstract beliefs that we humans use to create our goals. Values are whatever drives us and can include family, faith or frivolity.
Because values are subjective, what people identify as important to keep is also subjective. For example, the dress I wore to my sister’s wedding reminded me of a wonderful day. However, when it no longer fit I gave it away because doing so was more consistent with my values of utility and helpfulness: I wanted the dress to go to someone who needed it and would use it. Someone who more strongly valued family and beauty might have prioritized keeping the dress because of the aesthetics and its link to a family event.
Additionally, we found that instead of challenging the reasons a person might have for keeping an item, it is helpful to instead focus on eliciting their reasons for discarding it and the goals they have for their home and their life.
Tips for sweeping away the old
My research on using motivational interviewing for decluttering and my observations from a current clinical trial on the approach point to some practical steps people can take to declutter their home. Although my work has been primarily with older adults, these tips should be helpful for people of all ages.
Start with writing out your values. Every object in your home should feel value-consistent for you. For example, if tradition and faith are important values for you, you might be more inclined to hold onto a cookbook that was made by the elders at your church and more able to let go of a cookbook you picked up on a whim at a bookstore.
If, instead, health and creativity are your core values, it might be more important to hold onto a cookbook of novel ways to sneak more vegetables into your diet.
Defining value-consistent goals for using your space can help to maintain motivation as you declutter. Are you clearing off your desk so you can work more efficiently? Making space on kitchen counters to bake cookies with your grandchildren?
Remember that sometimes your values will conflict. At those moments, it may help to reflect on whether keeping or discarding an object will bring you closer to your goals for the space.
Similarly, remember that values are subjective. If you are helping a loved one declutter, maintain a curious, nonjudgmental attitude. Where you might see a box filled with junk, your grandmother might see something filled with “toothpick holders and other treasures.”
For additional resources and information on hoarding disorder, visit the International OCD Foundation website.
Mary E. Dozier, Assistant Professor of Psychology, Mississippi State University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
Prof. Mary Dozier makes some powerful, and cogent, statements in this article. Especially that one’s values are subjective. Nevertheless, I think I should write out my values and see what they tell me.