Not the first and I’m sure it won’t be the last on this topic!
We are experiencing the first week of Summer’s heat.
Where it is going, temperature-wise, who knows but the consensus is that it is becoming warmer year on year.
So this seemed like a great post to republish. It was on The Conversation.
ooOOoo
Heat index warnings can save lives on dangerously hot days − if people understand what they mean

Micki Olson, University at Albany, State University of New York
You’ve probably heard people say, “It’s not the heat, it’s the humidity.” There’s a lot of truth to that phrase, and it’s important to understand it as summer temperatures rise.
Humidity doesn’t just make you feel sticky and uncomfortable – it also creates extra dangerous conditions on hot days. Together, too much heat and humidity can make you sick. And in severe cases, it can cause your body to shut down.
Meteorologists talk about the risk of heat and humidity using the heat index, but it can be confusing.
I’m a risk communication researcher. Here’s what you need to know about the heat index and some better ways meteorologists can talk about the risks of extreme heat.

What is the heat index, and how is it measured?
Heat index is the combination of the actual air temperature and relative humidity:
- Air temperature is how hot or cold the air is, which depends on factors such as the time of day, season of the year and local weather conditions. It is what your thermometer reads in degrees Celsius or Fahrenheit.
- Relative humidity compares how much water vapor is in the air with how much water vapor the air could hold at that temperature. It’s expressed as a percentage.
The heat index tells you what it “feels like” outside when you factor in the humidity. For example, if it’s 98 degrees Fahrenheit (36.7 Celsius) with 55% relative humidity, it might feel more like a scorching 117 F (47.2 C).
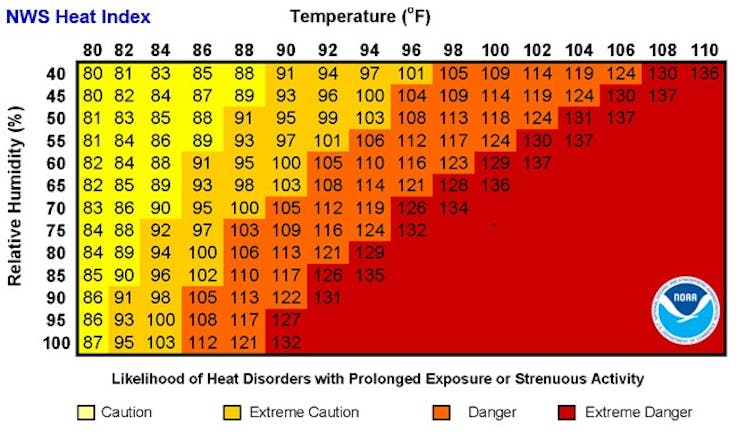
But there’s a catch: Heat index is measured in shady conditions to prevent the sun’s angle from affecting its calculation. This means if you’re in direct sunlight, it will feel even hotter.
Apparent temperature, alerts and wet bulb
“Apparent temperature” is another term you might hear this summer.
Apparent temperature is the “feels like” temperature. It considers not only temperature and humidity but also wind speed. This means it can tell us both the heat index and wind chill – or the combination of the temperature and wind speed. When conditions are humid, it feels hotter, and when it’s windy, it feels colder.
We found that apparent temperature is even less well understood than the heat index, possibly due to the word apparent having various interpretations.
There are a few other ways you may hear meteorologists talk about heat.
Wet bulb globe temperature considers temperature, humidity, wind and sunlight. It’s especially useful for those who spend time outdoors, such as workers and athletes, because it reflects conditions in direct sunlight.
HeatRisk is a new tool developed by the National Weather Service that uses colors and numbers to indicate heat risks for various groups. More research is needed, however, to know whether this type of information helps people make decisions.
In many places, the National Weather Service also issues alerts such as excessive heat watches, warnings and advisories.
The risk is getting lost in translation
Knowing about heat and humidity is important, but my colleagues and I have found that the term heat index is not well understood.
We recently conducted 16 focus groups across the United States, including areas with dry heat, like Phoenix, and more humid areas, like Houston. Many of the people involved didn’t know what the heat index was. Some confused it with the actual air temperature. Most also didn’t understand what the alerts meant, how serious they were or when they should protect themselves.
In our discussions with these groups, we found that meteorologists could get across the risk more clearly if, instead of using terms like heat index, they focus on explaining what it feels like outside and why those conditions are dangerous.
Watches, warnings and advisories could be improved by telling people what temperatures to expect, when and steps they can take to stay safe.
Climate change is exacerbating heat risks by making extreme heat more common, intense and long-lasting. This means clear communication is necessary to help people understand their risk and how they can protect themselves.
What you can do to protect yourself
With both hot and humid conditions, extra precautions are necessary to protect your health. When you get hot, you sweat. When sweat evaporates, this helps the body cool down. But humidity prevents the sweat from evaporating. If sweat cannot evaporate, the body has trouble lowering or regulating its temperature.
Although everyone is at risk of health issues in high heat, people over 65, pregnant women, infants and young children can have trouble cooling their bodies down or may run a higher risk of becoming dehydrated. Certain health conditions or medications can also increase a person’s risk of heat-related illness, so it’s important to talk to your doctor about your risk.
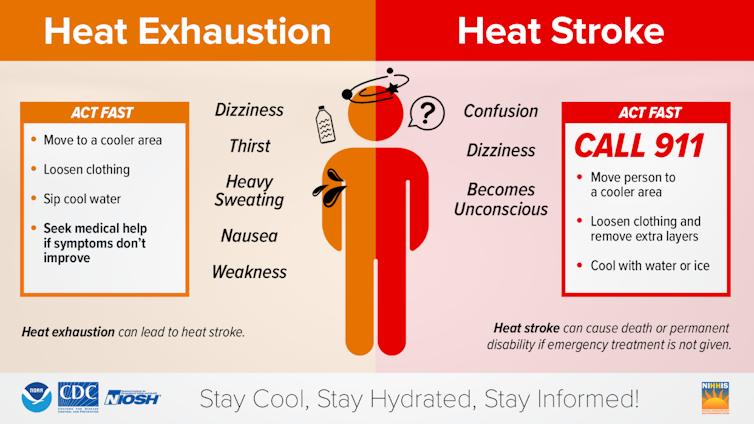
Heat illnesses, such as heat exhaustion and heat stroke, are preventable if you take the right steps. The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention focuses on staying cool, hydrated and informed.
- Stay cool: Use air conditioning in your home, or spend time in air-conditioned spaces, such as a shopping mall or public library. Limit or reschedule your exercise and other outdoor plans that occur in the middle of the day when it is hottest.
- Stay hydrated: Drink more water than you might otherwise, even if you don’t feel thirsty, so your body can regulate its temperature by sweating. But avoid sugary drinks, caffeine or drinks with alcohol, because these can cause you to become dehydrated.
- Stay informed: Know the signs of heat illness and symptoms that can occur, such as dizziness, weakness, thirst, heavy sweating and nausea. Know what to do and when to get help, because heat illnesses can be deadly.
Micki Olson, Senior Researcher in Emergency and Risk Communication, University at Albany, State University of New York
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
That last diagram on staying cool, staying hydrated, and staying informed is one element in me choosing this article for publication. Further, if one looks up the website for the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention then immediately one comes across:
Stay cool indoors.Stay in an air-conditioned place as much as possible. If your home does not have air conditioning, go to the shopping mall or public library—even a few hours spent in air conditioning can help your body stay cooler when you go back into the heat.
Please take care!
