Back to learning from our wonderful dogs.
Last week, on the 9th to be exact, I published a post under the title of What a funny lot we all are! The thrust of that post was the republication of a recent Tom Dispatch essay by Michael Klare: Tipping Points and the Question of Civilizational Survival. Professor Michael T. Klare is professor of peace and world security studies at Hampshire College and the author, most recently, of The Race for What’s Left. Those who read his essay will have found it a gloomy report on the future of mankind on this planet.
Back to my sub-title.
One of the golden pieces of advice for all of us who succumb to a fear of the future is to live in the present. Living in the now, in the present, is what our dogs do so very well, and it is a fabulous example for us humans. Because there is such a volume of news about so many things going wrong in our world, that it is easy to become overly negative, possibly to the point of causing us ill health, for there is strong link between mind and body.
When circumstances actually do change then dogs are incredibly quick to adapt to those changed times. Dogs, however, do not worry about the future.
All of which is my preamble to an essay that was published under The Conversation header on Sunday. It was an essay by Melanie Randle, and the link goes to a page that offers:
Melanie is an Associate Professor of Marketing in the School of Management, Operations and Marketing in the Faculty of Business at the University of Wollongong. Her primary research areas are social and non-profit marketing, particularly in the areas of volunteering and foster care. Other research interests include marketing to children, obesity and gambling.
That profile doesn’t give much of a heads-up to the theme of her essay. That theme, to my way of thinking, is that right now change is underway. A change in the awareness of people that change has to take place.
Which is why I chose part of a saying attributed to Plato for the title to this post. The full saying being:
“We can easily forgive a child who is afraid of the dark; the real tragedy of life is when men are afraid of the light.“
So to Melanie’s essay.
ooOOoo
Many fear the worst for humanity, so how do we avoid surrendering to an apocalyptic fate?
Melanie Randle, October 11, 2015
A new, four-nation study has found people rate the risks of global threats to humanity surprisingly high. These perceptions are likely to be important, socially and politically, in shaping how humanity responds to the threats.
The study, of more than 2000 people in the US, UK, Canada and Australia, found:
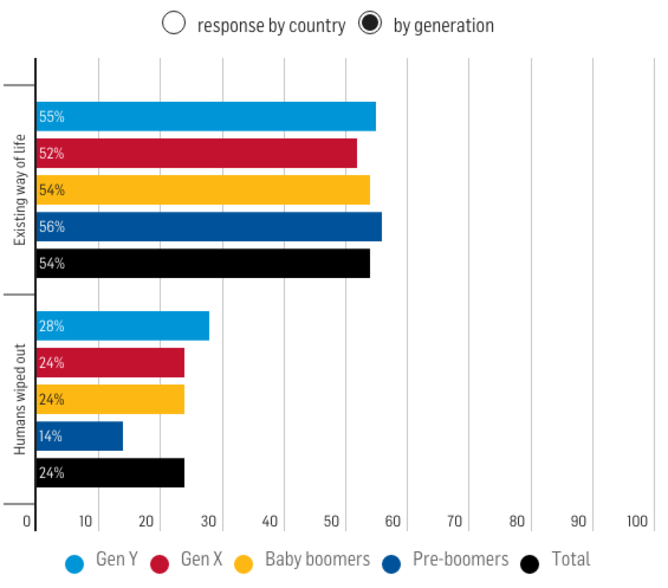
- 54% of people surveyed rated the risk of our way of life ending within the next 100 years at 50% or greater;
- almost one in four (24%) rated the risk of humans being wiped out within a century at 50% or greater;
- almost three in four (73%) believe there is a 30% or greater risk of our way of life ending (30% said that the risk is 70% or more); and
- almost four in ten (39%) believe there is a 30% or greater danger of humanity being wiped out (10% said the risk is 70% or more).
Perceptions of risks to way of life and humanity by country

The study also asked people about different responses to the threats. These responses were categorised as nihilism (the loss of belief in a social or moral order; decadence rules), fundamentalism (the retreat to certain belief; dogma rules), or activism (the transformation of belief; hope rules). It found:
- a large majority (78%) agreed “we need to transform our worldview and way of life if we are to create a better future for the world” (activism);
- about one in two (48%) agreed that “the world’s future looks grim so we have to focus on looking after ourselves and those we love” (nihilism); and
- more than one in three (36%) said “we are facing a final conflict between good and evil in the world” (fundamentalism).
Findings were similar across countries, age, sex and other demographic groups, although some interesting differences emerged. For example, more Americans (30%) believed the risk of humans being wiped out was high and that humanity faces a final conflict between good and evil (47%). This presumably reflects the strength in the US of Christian fundamentalism and its belief in the “end time”, a coming Apocalypse.
Perceptions of risk to way of life and humanity by generation
A world of threats coming to a head
There is mounting scientific evidence and concern that humanity faces a defining moment in history – a time when it must address growing adversities or suffer grave consequences. Reputable journals are canvassing the possibilities; the new study will be published in a special issue of Futures on “Confronting catastrophic threats to humanity”.
Most focus today is on climate change and its many, potentially catastrophic, impacts. Other threats include depletion and degradation of natural resources and ecosystems; continuing world population growth; disease pandemics; global economic collapse; nuclear and biological war and terrorism; and runaway technological change.
Many of these threats are not new. Scientists and other experts have warned of the dangers for decades. Nevertheless, the evidence is growing stronger, especially about climate change, and never before have actual events, including natural disasters and calamities, and their sustained and graphic media coverage so powerfully reinforced the possible impacts.
Not surprisingly, then, surveys reveal widespread public pessimism about the future of the world, at least in Western countries. This includes a common perception of declining quality of life, or that future generations will be worse off.
However, there appears to have been little research into people’s perceptions of how dire humanity’s predicament is, including the risk of collapse of civilisation or human extinction. These perceptions have a significant bearing on how societies, and humanity as a whole, deal with potentially catastrophic futures.
How does loss of faith in the future affect us?
People’s responses in our study do not necessarily represent considered assessments of the specific risks. Rather, they are likely to be an expression of a more general uncertainty and fear, a loss of faith in a future constructed around notions of material progress, economic growth and scientific and technological fixes to the challenges we face.
This loss of faith is important, yet hardly registers in current debate and discussion. We have yet to understand its full implications.
At best, the high perception of risk and the strong endorsement of an activist response could drive a much greater effort to confront global threats. At worst, with a loss of hope, fear of a catastrophic future erodes people’s faith in society, affecting their roles and responsibilities, and their relationship to social institutions, especially government.
It can deny us a social ideal to believe in – something to convince us to subordinate our own individual interests to a higher social purpose.
There is a deeply mythic dimension to this situation. Humans have always been susceptible to apocalyptic visions, especially in times of rapid change; we need utopian ideals to inspire us.
Our visions of the future are woven into the stories we create to make sense and meaning of our lives, to link us to a broader social or collective narrative. Historians and futurists have emphasised the importance of confidence and optimism to the health of civilisations and, conversely, the dangers of cynicism and disillusion.
Despite increasing political action on specific issues like climate change, globally the scale of our response falls far short of matching the magnitude of the threats. Closing this gap requires a deeper understanding of how people perceive the risks and how they might respond.
This article was co-authored by Richard Eckersley, founding director of Australia21.
ooOOoo
Now there’s nothing in the essay from Randle and Eckersley to say that these are not critically important times for all of humanity. Yet, I detect that among the many people one meets on a day-to-day basis there is a growing understanding that we can’t just lie down and let the future ride on over us. That living in the present and responding to the world around us here and now is the healthiest way to be, and the most effective. No more powerfully expressed than by Thich Nhat Hanh
“Fear keeps us focused on the past or worried about the future. If we can acknowledge our fear, we can realize that right now we are okay. Right now, today, we are still alive, and our bodies are working marvelously. Our eyes can still see the beautiful sky. Our ears can still hear the voices of our loved ones.”



