It is seemingly a simple question but in practice not so.
Listening to danger or telling others of a danger is a very ancient practice. For it is better to share a potential danger than not to. It was easy to look this up:
Modern sense of “risk, peril, exposure to injury, loss, pain, etc.” (from being in the control of someone or something else) evolved first in French and was in English by late 14c. For this, Old English had pleoh; in early Middle English this sense is found in peril. For sound changes, compare dungeon, which is from the same source.
Thus a post on The Conversation that was about happiness caught my eye.
I am delighted to share it with you.
ooOOoo
Philly psychology students map out local landmarks and hidden destinations where they feel happiest

Eric Zillmer, Drexel University
What makes you happy? Perhaps a good night’s sleep, or a wonderful meal with friends?
I am the director of the Happiness Lab at Drexel University, where I also teach a course on happiness. The Happiness Lab is a think tank that investigates the ingredients that contribute to people’s happiness.
Often, my students ask me something along the lines of, “Dr. Z, tell us one thing that will make us happier.”
As a first step, I advise them to spend more time outside.
Achieving lasting and sustainable happiness is more complicated. Research on the happiest countries in the world and the places where people live the longest, known as Blue Zones, shows a common thread: Residents feel they are part of something larger than themselves, such as a community or a city.
So if you’re living in a metropolis like Philadelphia, where, incidentally, the iconic pursuit of happiness charge was ratified in the Declaration of Independence, I believe urban citizenship – that is, forming an identity with your urban surroundings – should also be on your list.

Safety, social connection, beauty
Carl Jung, the renowned Swiss psychoanalyst, wrote extensively about the relationship between our internal world and our external environment.
He believed that this relationship was crucial to our psychological well-being.
More recent research in neuroscience and functional imaging has revealed a vast, intricate and complex neurological architecture underlying our psychological perception of a place. Numerous neurological pathways and functional loops transform a complex neuropsychological process into a simple realization: I am happy here!
For example, a happy place should feel safe.
The country of Croatia, a tourist haven for its beauty and culinary delights, is also one of the top 20 safest countries globally, according to the 2025 Global Peace Index.
The U.S. ranks 128th.
The availability of good food and drink can also be a significant factor in creating a happy place.
However, according to American psychologist Abraham Maslow, a pioneer in the field of positive psychology, the opportunity for social connectivity, experiencing something meaningful and having a sense of belonging is more crucial.
Furthermore, research on happy places suggests that they are beautiful. It should not come as a surprise that the happiest places in the world are also drop-dead gorgeous, such as the Indian Ocean archipelago of Mauritius, which is the happiest country in Africa, according to the 2025 World Happiness Report from the University of Oxford and others.
Happy places often provide access to nature and promote active lifestyles, which can help relieve stress. The residents of the island of Ikaria in Greece, for example, one of the original Blue Zones, demonstrate high levels of physical activity and social interaction.
Philly Happiness Map
I asked my undergraduate psychology students at Drexel, many of whom come from other cities, states and countries, to pick one place in Philadelphia where they feel happy.
From the 243 student responses, the Happiness Lab curated 28 Philly happy places, based on how frequently the places were endorsed and their accessibility.
Philadelphia’s founder, William Penn, would likely approve that Rittenhouse Square Park and three other public squares – Logan, Franklin and Washington – were included. These squares were vital to Penn’s vision of landscaped public parks to promote the health of the mind and body by providing “salubrious spaces similar to the private garden.” They are beautiful and approachable, serving as “places to rest, take a pause, work, or read a book,” one student told us.
Places such as the Philadelphia Zoo, Penn’s Landing and the Philadelphia Museum of Art are “joyful spots that are fun to explore, and one can also take your parents along if need be,” as another student described.
The Athenaeum of Philadelphia, a historic library with eclectic programming, feels to one student like “coming home, a perfect third place.”
Some students mentioned happy places that are less known. These include tucked-away gardens such as the John F. Collings Park at 1707 Chestnut St., the rooftop Cira Green at 129 S. 30th St. and the James G. Kaskey Memorial Park and BioPond at 433 S. University Ave.
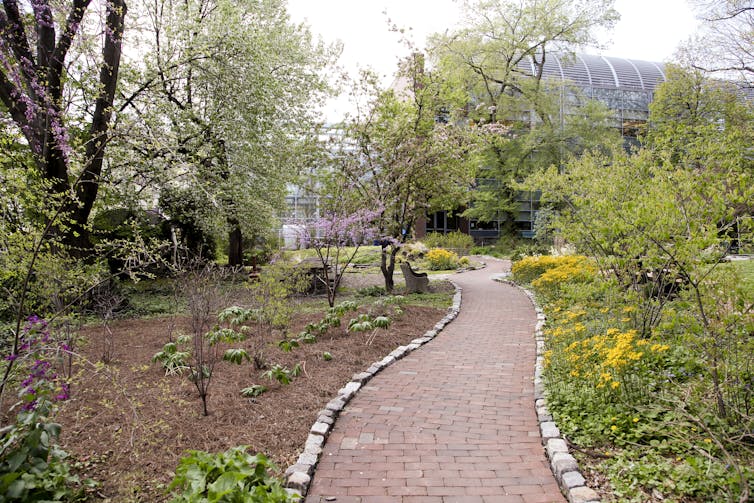

My students said these are small, unexpected spots that provide an excellent opportunity for a quiet, peaceful break, to be present, whether enjoyed alone or with a friend. I checked them out and I agree.
The students also mentioned places I had never heard of even though I’ve lived in the city for over 30 years.
The “cat park” at 526 N. Natrona St. in Mantua is a quiet little park with an eclectic personality and lots of friendly cats.
Mango Mango Dessert at 1013 Cherry St. in Chinatown, which is a frequently endorsed happiness spot among the students because of its “bustling streets, lively atmosphere and delicious food,” is a perfect pit stop for mango lovers. And Maison Sweet, at 2930 Chestnut St. in University City, is a casual bakery and cafe “where you may end up staying longer than planned,” one student shared.
I find that Philly’s happy places, as seen through the eyes of college students, tend to offer a space for residents to take time out from their day to pause, reset, relax and feel more connected and in touch with the city.
Happiness principals are universal, yet our own journeys are very personal. Philadelphians across the city may have their own list of happy places. There are really no right or wrong answers. If you don’t have a personal happy space, just start exploring and you may be surprised what you will find, including a new sense of happiness.
See the full Philly Happiness Map list here, and visit the exhibit at the W.W. Hagerty Library at Drexel University to learn more.
Read more of our stories about Philadelphia.
Eric Zillmer, Professor of Neuropsychology, Drexel University
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
For me, an Englishman living in Oregon, feeding the wild deer each morning gives me untold joy and happiness. It is my ‘personal happy space’.
So thank you, Prof. Zillmer, for writing this.
