It ought to be straightforward, but the reality is different!
Those of you, dear readers, that have been following these ramblings and musings over the last 30 months, now amounting to more than 1,200 Posts, will hopefully have sensed that Learning from Dogs is much more than a blogsite about dogs! It is, as I say here, about truth, integrity, honesty and trust using dogs as a powerful metaphor for these essential qualities of a civilised society.
But perhaps there is no topic more challenging for people to determine the truth than the topic of man’s impact on the earth’s climate. I’m sure that millions intuitively sense that we are over-consuming ourselves to oblivion. That is where I come from. I am not a scientist, just a humble writer, and rely on quality sources of information and instinct to form my conclusions in this area. I am also deeply suspicious of the largely out-of-sight relationships between large corporations, big money and politics!
I have no doubt that there are other millions of people who do believe that mankind is changing our planet’s climate.
So when I saw this article in the Wall Street Journal, I was dumbstruck. Here’s the headline and opening paragraph,
No Need to Panic About Global Warming
There’s no compelling scientific argument for drastic action to ‘decarbonize’ the world’s economy.
Editor’s Note: The following has been signed by the 16 scientists listed at the end of the article:
A candidate for public office in any contemporary democracy may have to consider what, if anything, to do about “global warming.” Candidates should understand that the oft-repeated claim that nearly all scientists demand that something dramatic be done to stop global warming is not true. In fact, a large and growing number of distinguished scientists and engineers do not agree that drastic actions on global warming are needed.
The long article closes with this paragraph just ahead of the ‘signatures’ of the scientists.
Every candidate should support rational measures to protect and improve our environment, but it makes no sense at all to back expensive programs that divert resources from real needs and are based on alarming but untenable claims of “incontrovertible” evidence.
Then in short order, up came this from the Daily Mail online,
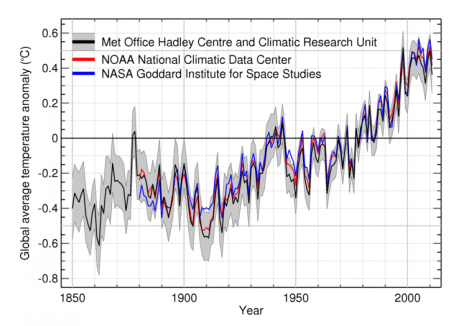
The supposed ‘consensus’ on man-made global warming is facing an inconvenient challenge after the release of new temperature data showing the planet has not warmed for the past 15 years.
The figures suggest that we could even be heading for a mini ice age to rival the 70-year temperature drop that saw frost fairs held on the Thames in the 17th Century.
Based on readings from more than 30,000 measuring stations, the data was issued last week without fanfare by the Met Office and the University of East Anglia Climatic Research Unit. It confirms that the rising trend in world temperatures ended in 1997.
I subscribe both to Climate Sight and Lack of Environment, although wish I spent more time thoroughly reading these fabulous sources of information. However, I did spot an article on Climate Sight that came out on the 31st January with the heading of How much is most? It opened thus,
A growing body of research is showing that humans are likely causing more than 100% of global warming: without our influences on the climate, the planet would actually be cooling slightly.
In 2007, the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change published its fourth assessment report, internationally regarded as the most credible summary of climate science to date. It concluded that “most of the observed increase in global average temperatures since the mid-20th century is very likely due to the observed increase in anthropogenic greenhouse gas concentrations”.
A clear question remains: How much is “most”? 51%? 75%? 99%? At the time that the IPCC report was written, the answer was unclear. However, a new frontier of climate research has emerged since, and scientists are working hard to quantify the answer to this question.
The timing was impeccable, so far as I was concerned. I posted a comment, “While in every way that I can think of, I support the premise of mankind affecting global climate, I would love to hear from someone who could reconcile the Post above with these recent items:” and then included the links to the WSJ and Daily Mail items.
Little did I realise what a response I would get. Just wonderful! I will offer some of them to you in this piece, but please do read all the comments offered on that Climate Sight post.
First up was Dana Nuccitelli. Dana is an environmental scientist at a private environmental consulting firm in the Sacramento, California area. He has a Bachelor’s Degree in astrophysics from the University of California at Berkeley, and a Master’s Degree in physics from the University of California at Davis. (Taken from here.) This is what he wrote,
How to reconcile the two? The folks who wrote those two articles you linked are misinformed and/or misinformers. I covered the first here (and) SkS will shortly have a post on the second as well, but I covered the solar cycle issue recently here.
Dana’s article in Skeptical Science, that first link, included this:
Nearly half of the list (at least 7 of 16) have received fossil fuel industry funding, and the list also includes an economist, a physician, a chemist, an aerospace engineer, and an astronaut/politician. These are apparently the best and brightest the climate denialists can come up with these days?
- Claude Allegre, former director of the Institute for the Study of the Earth, University of Paris
- J. Scott Armstrong, cofounder of the Journal of Forecasting and the International Journal of Forecasting;
- Jan Breslow, head of the Laboratory of Biochemical Genetics and Metabolism, Rockefeller University;
- Roger Cohen, fellow, American Physical Society;
- Edward David, member, National Academy of Engineering and National Academy of Sciences;
- William Happer, professor of physics, Princeton;
- Michael Kelly, professor of technology, University of Cambridge, U.K.;
- William Kininmonth, former head of climate research at the Australian Bureau of Meteorology;
- Richard Lindzen, professor of atmospheric sciences, MIT;
- James McGrath, professor of chemistry, Virginia Technical University;
- Rodney Nichols, former president and CEO of the New York Academy of Sciences;
- Burt Rutan, aerospace engineer, designer of Voyager and SpaceShipOne;
- Harrison H. Schmitt, Apollo 17 astronaut and former U.S. senator;
- Nir Shaviv, professor of astrophysics, Hebrew University, Jerusalem;
- Henk Tennekes, former director, Royal Dutch Meteorological Service;
- Antonio Zichichi, president of the World Federation of Scientists, Geneva.
RED – No climate science publications, member of at least one climate denialist group – GWPF (advisory board), George C. Marshall Institute (board of directors or roundtable speakers), Australian Climate Science Coalition (advisory panel), Heartland Institute (board of directors), and/or ExxonMobil
BLUE – Published climate science research
Orange – both a member of a climate denialist group and has published climate science research
Black – no climate science publications or climate denialist group membership
Next was Gail Zawacki who writes a compelling Blog Dead Trees and Dying Forests. She commented thus,
Paul, try climate progress, first link here and second link here. I suggest you read those refutations very carefully.
The first link went to this,
Panic Attack: Murdoch’s Wall Street Journal Finds 16 Scientists to Push Pollutocrat Agenda With Long-Debunked Climate Lies
By Joe Romm on Jan 29, 2012 at 12:33 pm
A lot of folks have asked me to debunk the recent anti-truthful Wall Street Journal article with the counterfactual headline, “No Need to Panic About Global Warming.” I’ll combine my debunking with the rapidly growing list of debunkings from scientists and others. And I’ll update this as new debunkings come in.
That the WSJ would publish an amateurish collection of falsehoods and half truths is no surprise. The entire global Murdoch enterprise is designed to advance the pollutocrat do-nothing agenda (see Scientist: “The Murdoch Media Empire Has Cost Humanity Perhaps One or Two Decades in Battle Against Climate Change”). As National Academy of Sciences member Peter Gleick explains in his evisceration of the piece, “Remarkable Editorial Bias on Climate Science at the Wall Street Journal“:
But the most amazing and telling evidence of the bias of the Wall Street Journalin this field is the fact that 255 members of the United States National Academy of Sciences wrote a comparable (but scientifically accurate) essay on the realities of climate change and on the need for improved and serious public debate around the issue, offered it to the Wall Street Journal, and were turned down. The National Academy of Sciences is the nation’s pre-eminent independent scientific organizations. Its members are among the most respected in the world in their fields. Yet the Journal wouldn’t publish this letter, from more than 15 times as many top scientists. Instead they chose to publish an error-filled and misleading piece on climate because some so-called experts aligned with their bias signed it. This may be good politics for them, but it is bad science and it is bad for the nation.
Science magazine – perhaps the nation’s most important journal on scientific issues – published the letter from the NAS members after the Journal turned it down.
A tad more surprising is that 16 admittedly non-leading scientists would choose to soil their reputations by stringing together a collection of long-debunked falsehoods. What is surprising is that these falsehoods are more easily debunked than the typical disinformer clap-trap because they are so out-of-date!
This is a long, detailed and powerful response to that WSJ article. Do try and read it in full.
Gail’s second link went to this,
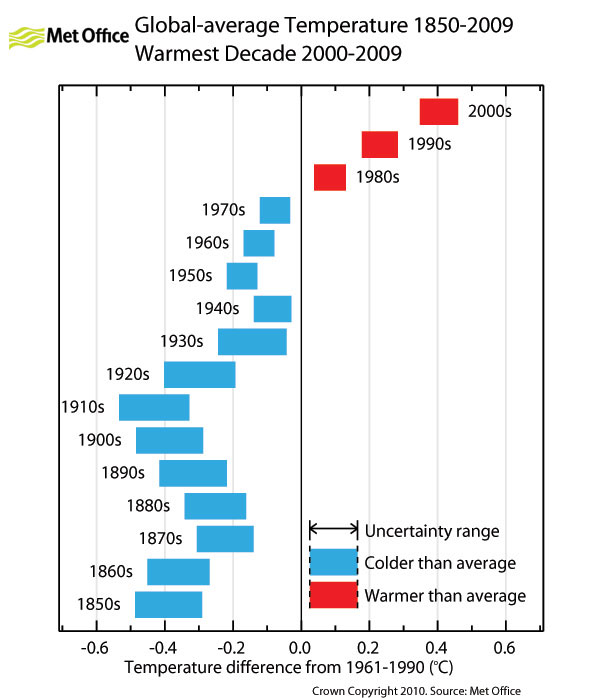
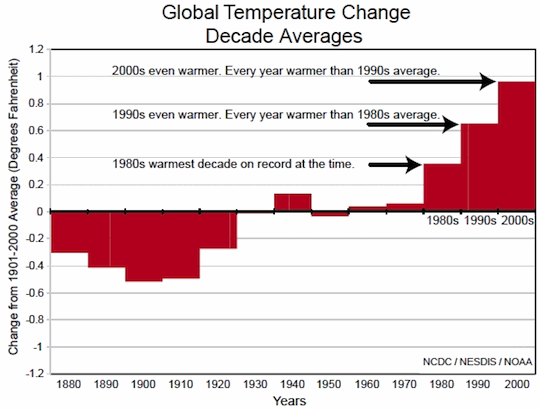
Human emissions of heat-trapping greenhouse gases have risen so rapidly that they now overwhelm any plausible decrease in solar activity. Indeed, a paper from last June found that even if the Sun goes into “Hibernation” it won’t stop catastrophic global warming.
But that doesn’t stop serial disinformer David Rose of the UK’s Daily Mail from misleading the public — even after being slammed by top scientists in 2010 for falsely asserting “no global warming since 1995″ — see “Error-riddled articles and false statements destroy Daily Mail’s credibility.“ Rose has another willfully misleading piece, “Forget global warming – it’s Cycle 25 we need to worry about (and if NASA scientists are right the Thames will be freezing over again): Met Office releases new figures which show no warming in 15 years.”
OK, I think this is going to end up too long for one Post.
So let’s pause there and I will continue on Monday.
Would love your comments, of course!