This gorgeous dog is up for adoption.
oooo
He is about 20 months old, a Husky and Shepard mix. Well mannered and sweet.
Please, if someone is keen to know more then please contact Carl at +1 (541) 415 0409.
Dogs are animals of integrity. We have much to learn from them.
Year: 2025
The role of the planet today!
From that post: Venus, named for the Roman goddess of love, reaches its greatest brilliancy on Valentine’s Day, February 14. Venus is currently blazing, low in the west after sunset, with Saturn below.
Wherever you are, try spotting Venus.
Namely a universal law.
I was attracted to an article that I read in The Conversation last a week ago.
It also taught me that we humans speak according to Zipf’s Law. I had not previously heard of this law.
So let me republish the article with the full permission of The Conversation.
ooOOoo

Jenny Allen, Griffith University; Ellen Garland, University of St Andrews; Inbal Arnon, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and Simon Kirby, University of Edinburgh
All known human languages display a surprising pattern: the most frequent word in a language is twice as frequent as the second most frequent, three times as frequent as the third, and so on. This is known as Zipf’s law.
Researchers have hunted for evidence of this pattern in communication among other species, but until now no other examples have been found.
In new research published today in Science, our team of experts in whale song, linguistics and developmental psychology analysed eight years’ of song recordings from humpback whales in New Caledonia. Led by Inbal Arnon from the Hebrew University, Ellen Garland from the University of St Andrews, and Simon Kirby from the University of Edinburgh, We used techniques inspired by the way human infants learn language to analyse humpback whale song.
We discovered that the same Zipfian pattern universally found across human languages also occurs in whale song. This complex signalling system, like human language, is culturally learned by each individual from others.
When infant humans are learning, they have to somehow discover where words start and end. Speech is continuous and does not come with gaps between words that they can use. So how do they break into language?
Thirty years of research has revealed that they do this by listening for sounds that are surprising in context: sounds within words are relatively predictable, but between words are relatively unpredictable. We analysed the whale song data using the same procedure.

Unexpectedly, using this technique revealed in whale song the same statistical properties that are found in all languages. It turns out both human language and whale song have statistically coherent parts.
In other words, they both contain recurring parts where the transitions between elements are more predictable within the part. Moreover, these recurring sub-sequences we detected follow the Zipfian frequency distribution found across all human languages, and not found before in other species.
Whale song recording (2017) Operation Cetaces 916 KB (download)
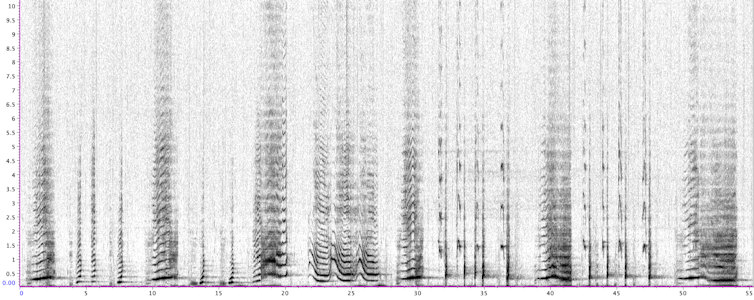
How do the same statistical properties arise in two evolutionarily distant species that differ from one another in so many ways? We suggest we found these similarities because humans and whales share a learning mechanism: culture.
Our findings raise an exciting question: why would such different systems in such incredibly distant species have common structures? We suggest the reason behind this is that both are culturally learned.
Cultural evolution inevitably leads to the emergence of properties that make learning easier. If a system is hard to learn, it will not survive to the next generation of learners.
There is growing evidence from experiments with humans that having statistically coherent parts, and having them follow a Zipfian distribution, makes learning easier. This suggests that learning and transmission play an important role in how these properties emerged in both human language and whale song.
Finding parallel structures between whale song and human language may also lead to another question: can we talk to whales now? The short answer is no, not at all.
Our study does not examine the meaning behind whale song sequences. We have no idea what these segments might mean to the whales, if they mean anything at all.
It might help to think about it like instrumental music, as music also contains similar structures. A melody can be learned, repeated, and spread – but that doesn’t give meaning to the musical notes in the same way that individual words have meaning.
Our work also makes a bold prediction: we should find this Zipfian distribution wherever complex communication is transmitted culturally. Humans and whales are not the only species that do this.
We find what is known as “vocal production learning” in an unusual range of species across the animal kingdom. Song birds in particular may provide the best place to look as many bird species culturally learn their songs, and unlike in whales, we know a lot about precisely how birds learn song.
Equally, we expect not to find these statistical properties in the communication of species that don’t transmit complex communication by learning. This will help to reveal whether cultural evolution is the common driver of these properties between humans and whales.
Jenny Allen, Postdoctoral research associate, Griffith University; Ellen Garland, Royal Society University Research Fellow, School of Biology, University of St Andrews; Inbal Arnon, Professor of Psychology, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, and Simon Kirby, Professor of Language Evolution, University of Edinburgh
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
ooOOoo
The research scientists have led to a prediction: … we should find this Zipfian distribution wherever complex communication is transmitted culturally. Humans and whales are not the only species that do this.
Fascinating!
A few last words from Paul!
I first met Richard Maugham when we were being treated to a private jet flight to the Hannover International Fair in 1982, some 43 years ago. We were both English and I was living in Tollesbury, Essex, near Colchester and Richard living near Ealing, West London.
The common thread was that all the passengers were major sellers of the Commodore ‘PET’.
Richard and I hit it off straight away. Richard was a fellow salesman. I was ex-IBM Office Products Division and Richard was ex-Olivetti.
Both of us also volunteered for the Prince’s Youth Business Trust, a charity headed by Prince of Wales, as he was then, helping young people start their own business.
Gillie and Colin, a couple who know Richard, recently sent me the following email:
Dear Paul,
I write to inform you that Richard passed away today at 2.50 GMT.
Both Colin and I were at his hospital bedside.
Our thoughts and condolences are with you.
Gillie and Colin.
The ‘today’ in the above email was Sunday, 9th February, 2025.
Richard will never be forgotten.
Richard will be sorely missed.